|
BPMN shape |
BPMN description |
|---|---|
|
|
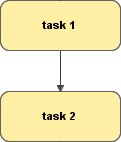
A Task is an atomic activity that is included within a process. A task is used in a BPMN diagram if the process can not be specified on a finer level of process model detail.
|
|
UML representation |
UML description |
|---|---|
|
|
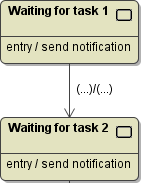
As already mentioned above, tasks are atomic from business point of view. However, from an execution point of view, this is not generally true. Actually, it is only true, if the task corresponds to a synchronous service call.
|
|
|
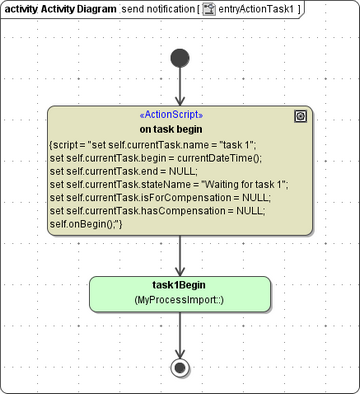
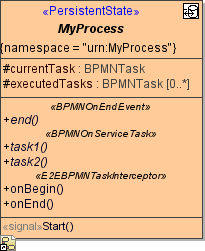
The handler of the state entry just calls an operation <task name>Begin.
|
|
|
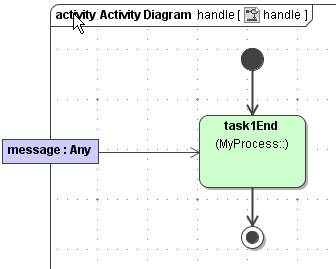
The signal handler calls an operation <task name>End when leaving the state.
|
|
|
The abstract <<PersistentState>> class contains the overridable operations that are invoked by each of the handlers. |
Not for all tasks it may make sense to wait for an acknowledge signal. For instance, service tasks just call a service. The following table shows the general mapping:
|
BPMN |
UML, generated state, handler and signal |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Task Type |
State Name |
Stereotype |
Entry Action |
Signal |
|
None |
Waiting for <task name> |
<<BPMNTask>> |
send notification |
<task name> Done |
|
Service |
Executed <task name> |
<<BPMNServiceTask>> |
call service |
./. |
|
Send |
Sending <task name> |
<<BPMNSendTask>> |
send<task name> |
./. |
|
Receive |
Waiting for <task name> |
<<BPMNReceiveTask>> |
./. |
<task name> Received |
|
User |
Waiting for <task name> |
<<BPMNUserTask>> |
send notification |
<task name> Done |
|
Script |
<task name> |
<<BPMNTask>> |
execute script |
./. |
Task type ![]()
Only unmarked tasks are supported yet. Marked tasks (as loop tasks, multiple instance tasks and compensation tasks) must be modeled explicitly.