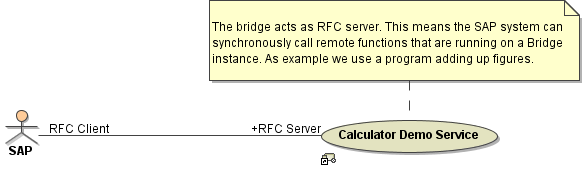
This is example shows how SAP calls remotely a function module running on the Bridge. This function module takes two numbers and returns their sum.
Figure: RFC Service Use Case
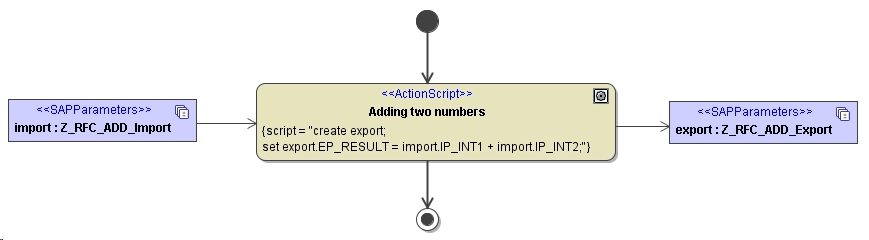
Implementing RFC Operations
The following example just adds two numbers. The only feature of this activity diagram being specific to SAP are the import and export parameters and the fact that is assigned to an operation of a <<SAPRFCModule>> class. These properties make this activity diagram callable from SAP systems. The only constraints on such activity diagrams are that their interface is restricted to import, export, changing and tables parameters (see RFC Arguments (SAP Service)).
Figure: Implementation of SAP RFC operation
The following classes give the import and export arguments:
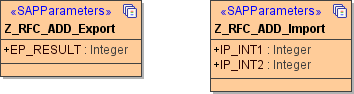
Defining RFC input- and output arguments are the same as for clients and are explained in chapter RFC Arguments (SAP Service).
RFC Service Components
In order to build a Bridge SAP RFC Server, the following components must be defined:
-
The xUML composite RFCServerExample holding all services you want to deploy.
-
Within the composite there are one or more SAP RFC services having the stereotype <<E2ESAPRFCService>>. In the current simple example it is the SAPRFCService.
-
Each service holds one or more classes with stereotype <<E2ESAPRFCModule>> that define the interface of the service. The activity diagrams assigned to the class operations define the implementation of the operations. In our example, the activity diagram Z_RFC_ADD implements the operation Z_RFC_ADD of the class. Z_RFC_SERVICES. Z_RFC_ADD is also the function name used within SAP ABAP programs to call the operation Z_RFC_ADD. See also the comment attached to the Z_RFC_ADD operation.
Builder 6 Modeling RFC services follows the same rules as modeling tRFC servers with two exceptions: the protocol tagged value must be rfc and there exists no <<SAPTRFCCallback>> interface.
Figure: RFC Service Components
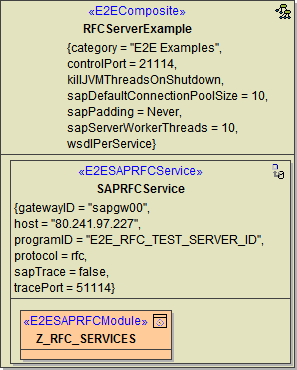
The RFCService has the following tagged values:
There were errors rendering macro: An unknown error occurred.
There were errors rendering macro: An unknown error occurred.
Example of an ABAP Function
The following example ABAP function (Z_CALL_RFC_SERVER) calls the Z_RFC_ADD Bridge operation by using the following ABAP code:
FUNCTION Z_CALL_RFC_SERVER.
*"----------------------------------------------------------------------
*"Local interface:
*" IMPORTING
*" VALUE(IP_VALUE1) TYPE I DEFAULT 0
*" VALUE(IP_VALUE2) TYPE I DEFAULT 0
*" EXPORTING
*" VALUE(EP_SUM) TYPE I
*"----------------------------------------------------------------------
DATA: EP_RESULT TYPE i VALUE 0.
CALL FUNCTION 'Z_RFC_ADD'
DESTINATION 'E2E_RFC_TEST_SERVER2'
EXPORTING IP_INT1 = IP_VALUE1
IP_INT2 = IP_VALUE2
IMPORTING EP_RESULT = EP_SUM.
ENDFUNCTION
