This page explains the REST Adapter in Bridge context. If you were looking for the same information regarding the PAS Designer, refer to REST Adapter in the Designer guide.
REST (Representational State Transfer) is a way to provide access to web resources using a uniform and predefined set of stateless operations. Refer to the Wikipedia pages of Representational State Transfer for more information on REST.
The Bridge has a REST protocol adapter ready. It enables you to use any REST service as a backend for the Bridge.
Today, there are already many services, which speak REST. You may also have several Bridge services that speak together via REST (for instance as part of a Software Oriented Architecture (SOA) environment).
For more information on how to implement a Web service that speaks REST, refer to REST Service.
Importing the Web Service Interface
Each Web service has its own distinct interface: in case of a REST service, defined by the names of the resources, their operations and their parameters. Before an external Web service can be used, its interface definition must be imported to the UML model. With the Builder, you can import OpenAPI 2.0 Specification service descriptors encoded in YAML (Swagger) (for more information see Importing OpenAPI Files REST).
The example REST service used below comes from our REST examples:
On importing the OpenAPI of the example REST service REST_SupportManagerExample to a UML model, the Builder places the interface definition of the service in a service repository RESTService.SupportAPI.yaml. The nodes in that package are the graphical representation of the definitions in the OpenAPI file.
Figure: Imported RESTful Web Service
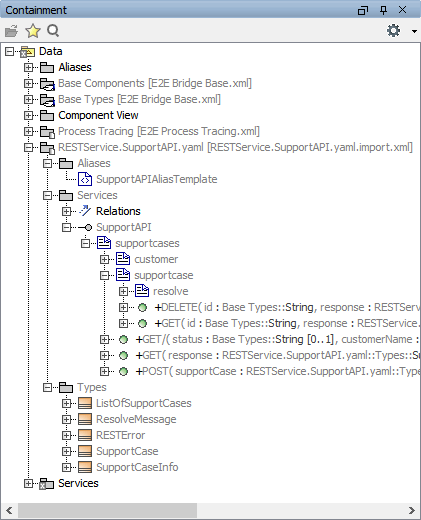
The REST service itself is displayed as an interface (SupportAPI). This interface features three resources (supportcases, customer and resolve) and their REST operations.
All input and output data structures are stored in a package Types.
Import Problems
The REST Service Only Provides a JSON Definition File
The xUML REST Importer can import YAML files only. If the service you want to call provides an OpenAPI file in JSON only, you can convert the JSON file to YAML before importing it. You can find many JSON to YAML converters on the internet.
The YAML File Does Not Set All Necessary Options
After having imported a YAML file, it may that some special options (like e.g. isVerbatimPath or externalName) that are not part of the official Open API description, are not set, but may be necessary.
Also, blob parameters, Blob Body Content Type/Reject Other Response Content Type and Accepted Request Content Type/Reject Other Request Content Types as described on Handling Blobs in the REST Interface are not supported by the importer.
In these cases, you will have to edit the import file manually to add blob parameters and set these options.
The Import of the YAML File Fails Or The REST Service Provides No Description File At All
It may be that the import of the YAML file fails or the REST service provides no description file at all. In this case, you can
-
draw the definitions manually by following the descriptions at Manually Providing the REST Interface ...
-
try an API design tool, the API Design Tool of Swagger. You can either check and rectify the YAML file here or write a new YAML file matching the service interface.
Accessing the Imported Web Service
An imported REST service can be accessed via a REST Adapter call as shown in the picture below.
Figure: REST Adapter Call
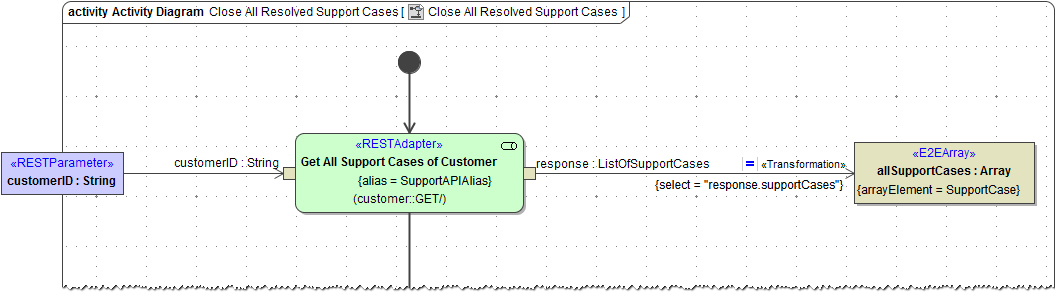
Apply stereotype <<RESTAdapter>> to call REST services and assign an alias to provide a path to the service to be called.
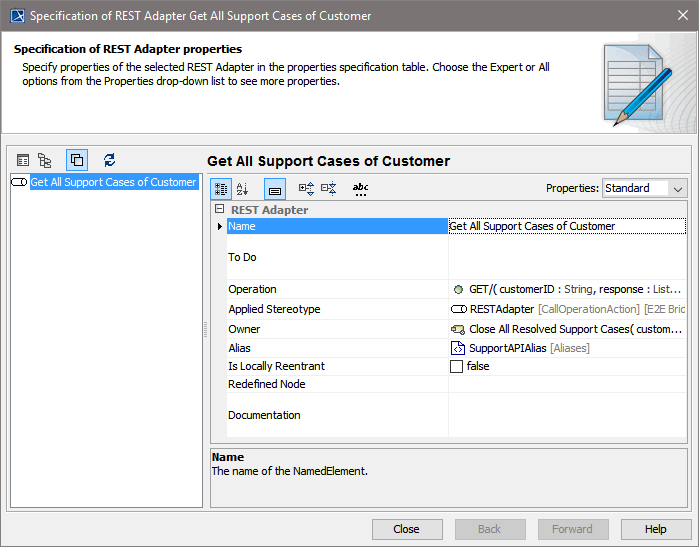
The Operation property contains the REST operation to be called, means one of the imported REST operations, see Figure: Imported RESTful Web Service. The response of an REST adapter call can be either of complex type or a Blob.
An activity diagram like that will also be generated, if you choose option import to new model on importing the REST service description.
For a detailed overview on all REST parameters, refer to REST Service Reference.
UML classes are mapped to the REST adapter call as described on XML - UML Class Mapping.
HTTP Headers
Runtime 2019.9 With xUML service adapter calls, the xUML Runtime adds the following outgoing HTTP headers containing correlation information to the request:
-
X-Transaction-Id or xTransactionId (in JMS context)
This header identifies the transaction the call belongs to. You can set the transaction id manually with setTransactionID() Operation. If not set, the Runtime will generate one.
This header will be passed through the callstack to identify all service calls that belong to a transaction. -
X-Request-Id
This header identifies the unique request. The Runtime generates a unique number for each adapter call. -
X-Sender-Host and X-Sender-Service
These headers contain the sender host resp. the sender service. They are set by the Runtime automatically.
Transaction id and request id will be logged to the transaction log on the adapter call. Having this information, you can use this for error analysis or usage metrics.
Builder 7.12.0 Runtime 2020.12 You can overwrite this default behavior by own header role definitions as described on HTTP Header Support > Overwriting the Standard HTTP Headers. In this context, you can also enable automatic header generation for dedicated headers.To do this, specify a list of header generation rules in tag requestHttpHeaderRoles on the REST alias.
requestHttpHeaderRoles can hold a list of definitions in format <http header name>:<role>. The listed headers will automatically be generated with the specified role for each adapter call on this alias. These definitions overwrite the default behavior, and X-Transaction-Id, X-Request-Id, X-Sender-Host and/or X-Sender-Service will be substituted by this definition.
Refer to REST Adapter Reference for the list of allowed values.
Also note the implications of Blob Body Content Type/Reject Other Response Content Type and Accepted Request Content Type/Reject Other Request Content Types as described on Handling Blobs in the REST Interface.
REST Adapter Components
The location of the REST service and other settings to access the service are provided in the component diagram on a REST alias. You can link these definitions in the component diagram to the implementation in an activity diagram via the tagged value alias on the corresponding activity.
Figure: REST Adapter Components
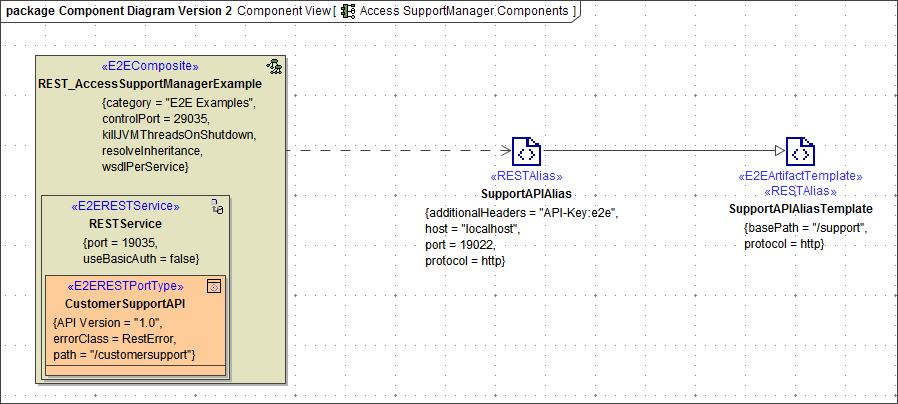
The REST service import provides an alias template you can derive the actual alias from (see picture above). Draw a new REST alias as described on Backend Components > Creating an Alias and draw a generalization from this alias to the template.
The <<RESTAlias>> can hold the following tagged values:
AttributeDescriptionAllowed ValuesAdditional Headers (additionalHeaders)This tagged value can contain a list of additional headers in form of name/value pairs.Valid format is: <name>:<value>, e.g. API-Key:e2e. Separate multiple headers with a comma.Base Path (basePath)Specify here the base path of the REST service.a valid path, e.g. /supportProtocol (protocol)Specify here the protocol through which the REST service is accessible.http, httpsIgnore Http Errors (ignoreHttpErrors)Specify here whether you want the REST adapter to throw an exception upon receiving an HTTP error code >= 400.For older models, if this flag is not present, it will be considered false.ignoreHttpErrors can be overridden via the request options (see (26.0) Setting REST Request Options).true (default)Do not throw an exception upon receiving an HTTP error code >= 400.falseThrow an exception upon receiving an HTTP error code >= 400.Host (host)Specify here the host running the REST service.a valid hostPort (port)Specify here the port through which the REST service is accessible.a valid portFollow Redirects (followRedirects)Specify here the maximum number of redirects to follow. Default value is 0 (no redirects).any integerRequest Transfer EncodingSpecify whether to disable chunk encoding for POST, PUT, and PATCH requests.Set to none if the endpoint cannot handle chunked encoding. noneSend the request body as one continuous stream with a content-length header.chunkedSend the request body in multiple chunks (default).Options (options)Specify native cURL options as listed in (26.0) Setting cURL Options on the URL Adapter .Use one of the following syntax rules:values separated by ',' in one linevalues separated by ' ' in one linelist of tagged valuesJson Keep Nulls (jsonKeepNulls)When jsonKeepNulls is true, attributes of the REST parameter having NULL values will be provided with the REST call, otherwise they will be left out completely (see also chapter NULL Values).trueRender attributes with NULL values to the REST call.falseLeave out attributes with NULL values in the REST call (default).Json Compact (jsonCompact)When jsonCompact is true, the JSON composer will generate compact JSON, otherwise it will generate pretty JSON. jsonCompact defaults to true - also on re-compile of an older model with Builder as of 7.0.0-beta3.trueGenerate compact JSON (default).falseGenerate pretty JSON.Request Http Header Roles (requestHttpHeaderRoles)Builder 7.12.0 Runtime 2020.12 In the context of HTTP based adapters (URL, REST, SOAP), enable automatic header generation for the listed headers. These definitions overwrite the default behavior, and X-Transaction-Id, X-Request-Id, X-Sender-Host and/or X-Sender-Service will be substituted by this definition.requestHttpHeaderRoles can hold a list of definitions in format <http header name>:<role>, that will automatically be generated for each adapter call on this alias. <role> can be one of the listed allowed values (one list entry per line).Refer to HTTP Header Support > Overwriting the Standard HTTP Headers for more details on header roles.client_hostProvide the client host in a header <http header name> instead of X-Sender-Host.client_serviceProvide the client service in a header <http header name> instead of X-Sender-Service.correlation_idProvide the correlation ID in a header <http header name> instead of X-Request-Id.transaction_idProvide the transaction ID in a header <http header name> instead of X-Transaction-Id.passthroughPass a present header <http header name> to the called service.passthrough= <request header name> Pass an present header <request header name> to the called service under the name of <http header name>.This is equivalent to renaming a header.Digest Algorithm (digestAlgorithm)Runtime 2021.1 Builder 7.12.0 Generates a HTTP digest header using the specified algorithm. When applied, a digest header is generated using the specified algorithm, and sent with the request . The generated header conforms with RFC3230 and RFC5843. Only one value is supported (no multi-value header).NoneNo header generated.MD5Generate header using MD5 algorithm.SHAGenerate header using SHA algorithm.SHA-1Generate header using SHA-1 algorithm.SHA-256Generate header using SHA-256 algorithm.SHA-512Generate header using SHA-512 algorithm.User (user)Specify credentials here, if the called REST service needs basic authentication. Other authentication algorithms have to be implemented manually via HTTP headers (see additionalHeaders and (26.0) Setting REST Request Options).Valid format is <user>/<password>, e.g. e2e/e2eProxy Settings (if the called REST service is accessed via a proxy)Proxy Type (proxyType)Specify the proxy type.See CURLOPT_PROXYTYPE.Proxy URL (proxyURL)Specify the URL of the proxy server.See CURLOPT_PROXY.Proxy User (proxyUser)Specify the proxy credentials.See CURLOPT_PROXYUSERPWD, valid format is <user>/<password>, e.g. e2e/e2eSSL Settings (if the called REST service uses SSL)Ssl CA Info (sslCAInfo)Specify a file name containing additional certificates for the connection verification (e.g. additional root CAs).See CURLOPT_CAINFO.Ssl Certificate File (sslCertificateFile)Specify a fle name containing the client certificate.See CURLOPT_SSLCERT.Ssl Certificate Type (sslCertificateType)Specify the type of the certificate.See CURLOPT_SSLCERTTYPE.Ssl Private Key File (sslPrivateKeyFile)Specify a file name containing the private key.See CURLOPT_SSLKEY.Ssl Private Key Password (sslPrivateKeyPassword)Specify the password for the private key.See CURLOPT_KEYPASSWD.Ssl Private Key Type (sslPrivateKeyType)Specify the type of the key.See CURLOPT_SSLKEYTYPE.Ssl Verify Host (sslVerifyHost)Specify whether to verify the host information form the SSL connection.See CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYHOST.Ssl Verify Peer (sslVerifyPeer)Specify whether to verify the peer information from the SSL connection.See CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER.
If you want to overwrite these tags dynamically during service execution, refer to Setting REST Request Options for more details.
