Number Formatting is used by <<FlatFile>> parser and composer and Integer, Float and String objects (e.g. parseFloatExpression(), printFloatExpression(), parseIntegerExpression(), printIntegerExpression()).
The format processor uses similar patterns as Oracle and PostgreSQL but is not 100% compatible e.g. there's no support for scientific and roman notation.
All parse and compose functionality is influenced by locales. The <<FlatFile>> adapter and the parse and print number operations take a parameter of type Basic Components::Basic Behavior::NumbersLocale. This parameter can be used to define
|
Class |
Attribute |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NumbersLocale |
negativeSign |
String |
Characters used to signify negative values. Usually ' |
|
positiveSign |
String |
Characters used to signify positive values. Usually ' |
|
|
thousandsSeparator |
String |
Characters used to separate units of thousand, e.g. ' |
|
|
decimalPoint |
String |
e.g. ' |
|
|
currencySymbol |
String |
e.g. ' |
Default values are given by the system locales.
To specify a number format, the attribute must have stereotype <<FlatFileAttribute>>.
Figure: Specifying a Format Tagged Value on a Class Attribute
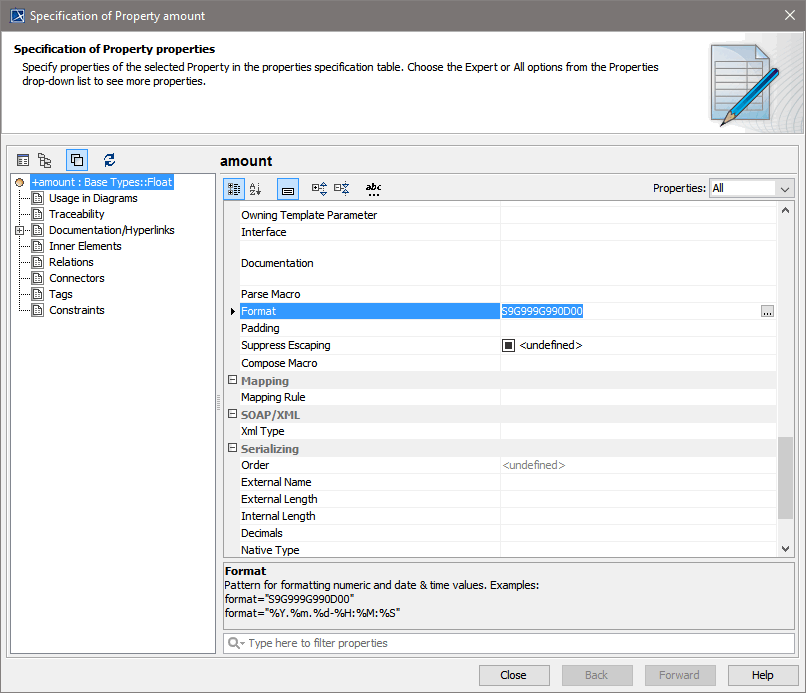
Locale characters are by default the system locales. These can be overridden by providing a Locale structure as input parameter to flatfile parser/composer or script function.
Patterns
This table shows the template patterns available for formatting numeric values.
|
Pattern |
Description |
|---|---|
|
9 |
Value with the specified number of digits. |
|
0 |
Value with leading zeros. |
|
. (period) |
Decimal point. |
|
, (comma) |
Group (thousand) separator. |
|
PR |
Negative value in angle brackets. |
|
S |
Sign anchored to number (uses locale). |
|
L |
Currency symbol (uses locale). |
|
D |
Decimal point (uses locale). |
|
G |
Group separator (uses locale). |
|
MI |
Minus sign in specified position (if number < 0). |
|
PL |
Plus sign in specified position (if number > 0). |
|
SG |
Plus/minus sign in specified position. |
|
TH or th |
Ordinal number suffix. |
|
V |
Shift specified number of digits (see notes). |
|
FM |
Fill mode prefix, will discard any leading spaces. |
Usage Notes
-
A sign formatted using SG, PL, or MI is not anchored to the number; for example,
to_char(-12, 'S9999')produces ' -12', butto_char(-12, 'MI9999')produces '- 12'. -
9 results in a value with the same number of digits as there are 9s. If a digit is not available it outputs a space.
-
TH does not convert values less than zero and does not convert fractional numbers.
-
V effectively multiplies the input values by 10^n, where n is the number of digits following V.
to_char()does not support the use of V combined with a decimal point. (E.g., 99.9V99 is not allowed.) -
Locale characters are by default the system locales. These can be overriden by providing a Locale structure as input parameter to flatfile parser/composer or script function.
Examples
You can test your own format expression with the above mentioned example.
The following locale is used:
-
Negative sign "-"
-
Positive sign "+"
-
Thousands separator " "
-
Decimal point ","
-
Currency symbol "$"
|
Number |
Format |
Output String |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parsing not possible. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
no leading zeros ( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
leading blank comes from the plus sign, that is not displayed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
hard coded group separator |
|
|
|
|
group separator from locale |
|
|
|
|
hard coded decimal point |
|
|
|
|
decimal point from locale |
|
|
|
|
group separator and decimal point from locale |
|
|
|
|
value increased by factor 1000, because 3 digit are following the specification of |
|
|
|
|
value increased by factor 1000, because 3 digit are following the specification of |
|
|
|
|
value increased by factor 10, because 1 digit is following the specification of |
|
|
|
|
displaying the sign from locale in rear of the number |
|
|
|
|
displaying a minus sign in rear of the number, if number is negative |
|
|
|
|
no minus sign added if number is positive, but empty space instead |
|
|
|
|
adding a plus sign in front of number if number is positive ( |
|
|
|
|
adding no plus sign in front of number because number is not positive (PL), negative system sign, no trimming of leading spaces |
|
|
|
|
displaying a plus sign in rear of the number, if number is positive ( |
|
|
|
|
displaying a plus sign in rear of the number, if number is positive ( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
displaying the currency symbol in front of the number ( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
