This page explains the MongoDB Adapter in Bridge context. If you were looking for the same information regarding the PAS Designer, refer to MongoDB Adapter in the Designer guide.
Use stereotype <<MongoDBAdapter>> on an action node to interact with a MongoDB and to insert, get and manipulate documents.
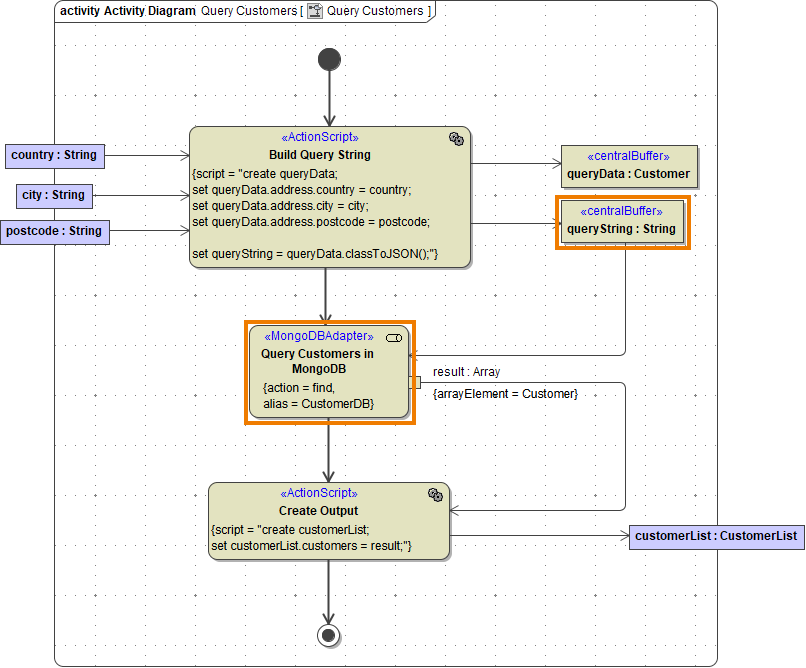
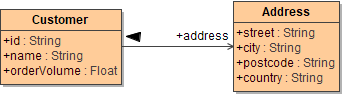
Using action find you can retrieve data. MongoDB stores data in form of documents that are depicted in a JSON-like format. Queries always return one or more complete documents.
For all actions that refer to existing documents, you need to provide a query string (queryString) to identify them. A query string contains all properties of the document you want to use for selection.
The simplest way to create a query string is to create an object having the structure of the document (queryData in the example above), and set all query values to this object.
Then, provide this object as queryString by converting it to JSON using classToExtendedJSON().
A find action of a <<MongoDBAdapter>> returns either a result set or a handle.
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
result |
Array of String |
An array of all resulting documents in JSON format. |
The complete set of found documents in an array. |
|
Array of <document class> |
An array of objects of an xUML class representing the document structure. This only makes sense if you know the structure of the documents you are accessing.
|
||
|
handle |
MongoDBHandle |
A handle to a result set. This is helpful if
|
You need to process the result set one by one using fetch. |
Refer to Action "find" and Action "fetch" for a detailed description of all parameters and options.
Selecting Output Data
MongoDB uses the concept of "projection" to define which properties should be selected from a document. The projection is supplied to the adapter call via the projection attribute of the MongoDBFindOptions.
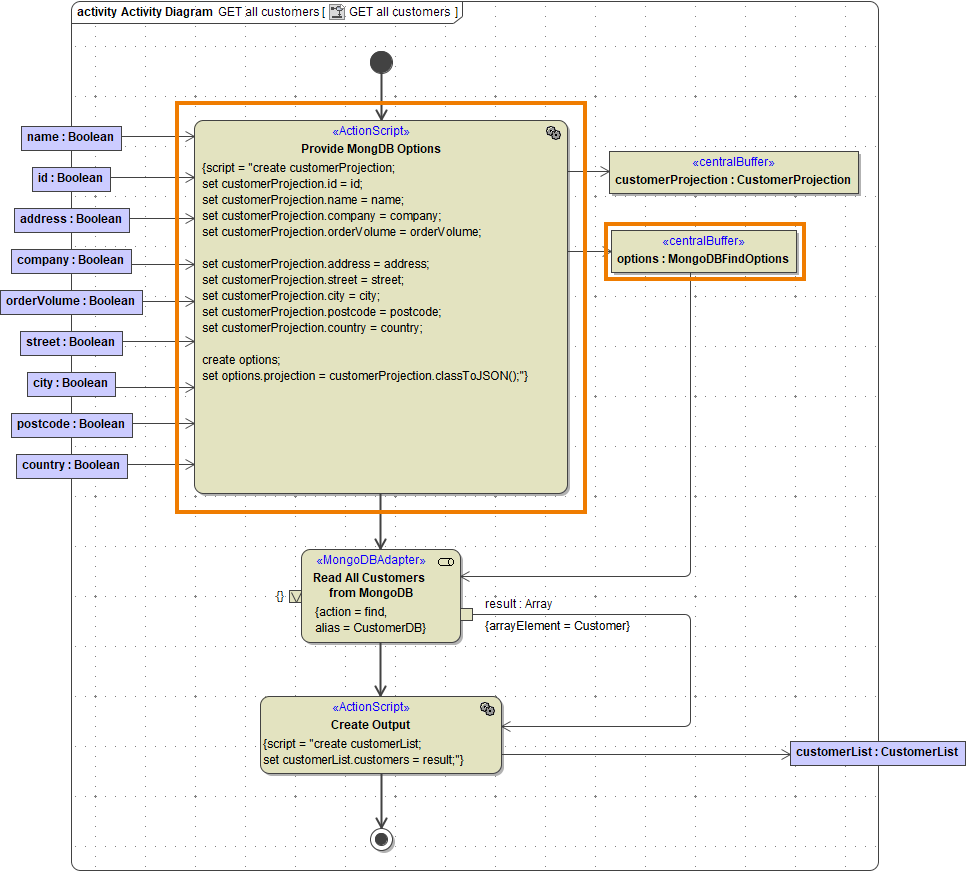
The following rules apply to projections:
|
Rule |
Example |
|---|---|
|
You can select dedicated properties. |
|
|
You can select all properties and omit dedicated properties. |
|
|
You cannot mix both above mentioned rules. This will lead to an exception. |
|
|
You can select properties from within a structure. |
|
|
You cannot select all properties and omit dedicated properties from within a structure. This will be ignored. |
|
Sorting
You can sort the document list you get back from an adapter call by providing the sort attribute of MongoDBFindOptions.
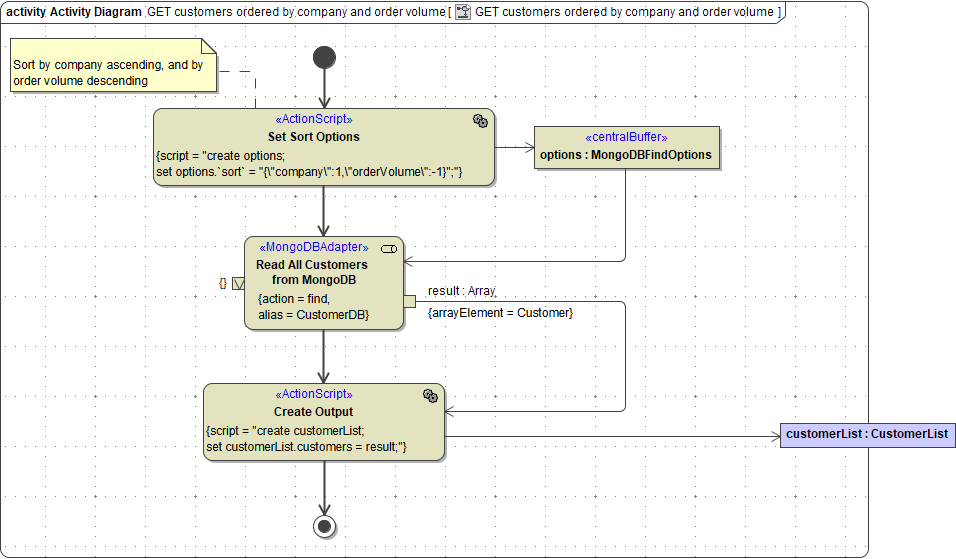
Parameter sort contains the document properties to sort by. Value 1 is ascending sorting, value -1 is descending sorting. The order of JSON properties reflects the sort hierarchy.
You need to escape the attribute name sort because there is an operation having the same name.
