Modeling tRFC clients is explained by an example showing how the Bridge can send IDocs to SAP. This is the most common use case for tRFC clients. The difference between tRFC and RFC is the additional transaction handling. This transaction handling must guarantee that one transaction can be executed only once.
In the simple example in the current UML model we show only how to use the transaction mechanism offered by SAP. The proper transaction control is implemented elsewhere (cf. the SAP module). The next section gives an overview of the components required to build a tRFC client.
Calling tRFC Functions
Accessing SAP via tRFC requires the following adapters:
|
Adapter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
<<SAPTRFCCreateTransaction>> |
This adapter tries to get a transaction ID from the SAP system.
|
|
<<SAPTRFCAdapter>> |
The tRFC Adapter takes all input data and the current transaction ID and sends them to the SAP system using the tRFC protocol. Possible input parameters are import and tables. Output parameters are not support because the tRFC protocol is asynchronous. In all other respects, the <<SAPTRFCAdapter>> works like the <<SAPRFCAdapter>>.
|
|
<<SAPTRFCConfirmTransaction>> |
This adapter confirms the successful termination of a transaction. It must be called only if no errors occurred during execution of the <<SAPTRFCAdapter>>.
|
In contrast to tRFC between SAP systems, a transaction from an RFC client must contain only one RFC function.
The activity diagrams that access the SAP system in the example file (SendAnyIDoc and SendTXTRAW) are the implementations of the SOAP Port Type IDocInterface. Both activity diagrams call IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS to send an IDoc to the SAP system (see for example figure below). The only difference is, that SendTXTRaw requires a TXTRAW IDoc as input whereas SendAnyIDoc the same input parameters.
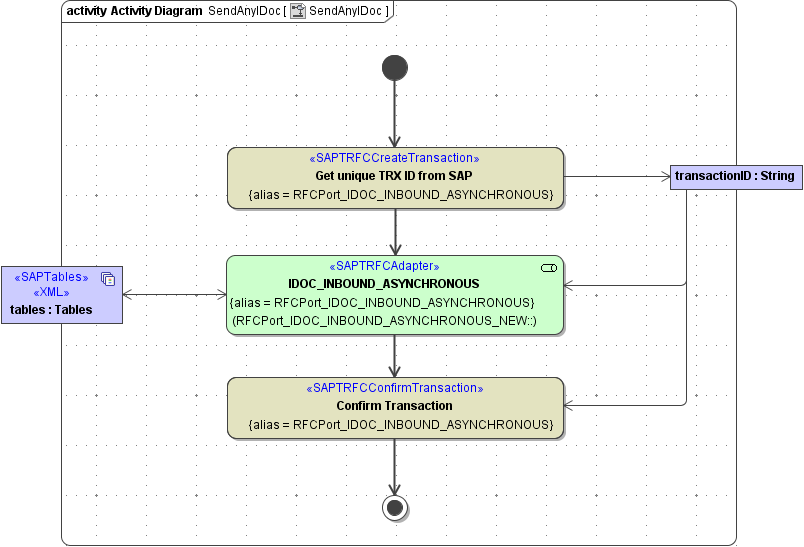
If you drag and drop the operation from the containment tree to the diagram pane, it will get the stereotype <<SAPRFCAdapter>>. To replace this with the desired stereotype <<SAPTRFCAdapter>> you have to remove the old stereotype first and then select the new one from the list, because <<SAPTRFCAdapter>> will not show up on the list of available stereotypes as long as <<SAPRFCAdapter>> is still selected.
tRFC Client Components
The components depicted in the figure below send IDocs from the frontend via tRFC to SAP. The frontend interface is SOAP. Therefore, the configuration holds a SOAP service component, namely saptRFCClientService. This component contains a SOAP IDocInterface whose operations do the actual calling of the SAP tRFC interface.
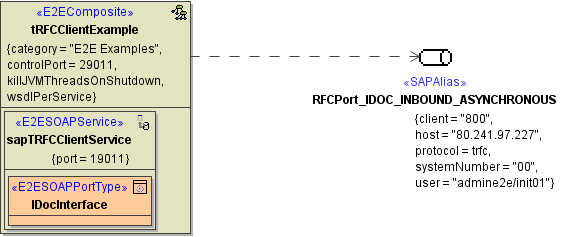
The component tRFCClientExample contains a SOAP service accessing the SAP system. This SAP system is modeled as an SAP Alias (RFCPort_IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS) used by the tRFC adapter.
The <<SAPAlias>> holds the following tagged values:
Tagged ValueDescriptionMandatory / OptionalAllowed ValuesprotocolSupply the connection protocolmandatoryrfcto use the RFC protocoltrfcto use the tRFC protocolhostSupply the gateway host name (optional).mandatoryany string, must be a valid SAP hostlocalhost (default)clientSupply the SAP logon client.mandatoryany string, must be a valid SAP clientuserSupply user and password.mandatoryany string matching the pattern "<user>/<password>"systemNumberSupply the system number of the SAP system.optionalany string, default = "00"routerStringThe router string is an additional routing information used by SAP RFC backend clients.SAP RFC clients prepend the DNS hostname with this string to get an application server name that is resolvable by the RFC library.optionalany stringpoolSizeRuntime 2015.10 Supply the maximum number of parallel connections to the SAP system.The pool size can be defined per connection string. If you have multiple aliases with the same connection string, the highest value will be used.The same applies, if you set the values in the SAP adapter settings on the Bridge.If this tag is not set, the connection pool size specified on the <<E2EComposite>> will be applied.Compatibility note: This tag will not be created for existing aliases in older models. You have to add the tag manually if you want to set it.Older xUML Runtimes (before version 2015.10) will not start with the setting being present. As a workaround, you can delete the tag value.If all connections from the SAP connection pool are in use, warnings will be logged to the transaction log each second a service is waiting for connection.2015-12-08 16:47:24 +0100 0000000182469dcd0001612899fea700e3d869aa 3 SAPConnectionPool 0 OK SAPRFC IO_ENTER PoolExhausted 2015-12-08 16:47:25 +0100 0000000182469dcd0001612899fea700e3d869aa 3 SAPConnectionPool 1000 OK SAPRFC IO_EXIT PoolExhaustedIn this case, increase the pool size to solve the problem.optionaldefault = 10languageSupply the SAP logon language.optional1-byte SAP language like E for English, D for German2-byte ISO language like EN for English, DE for GermansapTraceThe effect of this flag being true is two fold:First, the SAP RFC libraries will write trace file information (.trc) into the directory the service has been deployed to.Second, by using the SAP transaction *SMGW (SAP gateway monitor) we can monitor the dataflow from and to the gateway the server is registered on.The SAP trace level has to be defined in tagged value connectionString. See Client Connection Options for a list of the allowed trace level values.optionaloptionsA blank separated list of name value pairs: name1="value1" name2="value2", and so forth. The possible name value pairs can be found further below.optional
systemNumber and routerString can be found in the SAP GUI logon panel.
On the composite, you can also set a service-wide SAP value padding: Never, Always and Mixed. See Frontend Components for more information.
Client Connection Options
Via the SAP alias and the configuration descriptor we get the protocol and the connection string. This string looks like:
name1="value1" name2="value2" ...
The connection string must be provided in the following format:
<optionName>="<optionValue>"<space><optionName>="<optionValue>"...
Failure to conform with the pattern will lead unrecognized options. Those errors won't be reported, but affect SAP behavior (e.g. you'll get a SAP connection error with CALL_FUNCTION_SIGNON_INCOMPL).
Pay attention that the names are not case-sensitive but the values are. Depending on the RFC server, some of these names are fix and some of them are optional.
Following options are available :
|
Name |
Description |
Values |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
ABAP_DEBUG |
RFC with ABAP debugger |
0 |
without Debugger (default) |
|
1 |
with Debugger |
||
|
ASHOST |
Host name of a specific application server (R/3, No Load Balancing) |
|
|
|
CFIT |
Conversion Fault Indicator Token.
|
non Unicode systems 0x23,
|
|
|
CODEPAGE |
The given codepage is to be used for this connection (Default is either 1100 or set by RfcSetSystemCodepage or is set by SAP_CODEPAGE environment variable). Could be rather useful if the sapgui should be started with codepage differs from 1100. |
|
|
|
COMM_CP |
When communication has to be established between an Unicode Library and a Non Unicode system, all char like data will be converted into codepage which matched to logon language before send them.
|
|
|
|
DEST |
Destination in saprfc.ini if working with saprfc.ini. If the RFC server is an R/2 system this destination must also be defined in the 'sideinfo' for the SAP gateway. |
|
|
|
GROUP |
Name of the group of application servers (if using Load Balancing) |
|
|
|
GRT_DATA |
SAProuter connect data for SAPGUI when using RFC with SAPGUI. /H/...... : the whole router string for SAPGUI. /P/password: If the password for the SAPGUI connection is not the same as the one for the RFC connection. |
|
|
|
GWHOST |
Host name of the SAP gateway (if server is R/2 or External) |
|
|
|
GWSERV |
Service of the SAP gateway (if server is R/2 or External) |
|
|
|
ICCE |
Ignore Character Conversion Errors.
|
0 |
not ignore (default) or defined by environment variable RFC_IGNORE_CONV_ERROR) |
|
1 |
ignore |
||
|
IDLE_TIMEOUT |
Inform the Web Application Server to close the connection after idle time in seconds. |
|
|
|
LCHECK |
Logon check at OPEN time |
0 |
without check |
|
1 |
with check (default) |
||
|
MSHOST |
Host name of the Message Server (if using Load Balancing) |
|
|
|
MSSERV |
Service of the Message Server (if using Load Balancing) |
|
|
|
NEWPASS |
Changes the password during logon On SAP system kernel older than 46C the password is sent in clear text on the network! |
|
|
|
PCS |
Partner's Char Size. The RFC-library determines automatically the partner's char size at open time (using logon check) or at first call time (without logon check).
|
1 |
Non Unicode (default) |
|
2 |
Unicode |
||
|
R3NAME |
Name of the SAP system (if using Load Balancing) |
|
|
|
SAPLOGON_ID |
String defined for SAPLOGON on 32-bit Windows |
|
|
|
SNC_LIB |
Path and name of the SNC-library |
|
|
|
SNC_MODE |
Working with SNC |
0 |
without SNC (default, see RFC_SNC_MODE) |
|
1 |
with SNC |
||
|
SNC_MYNAME |
Own SNC name if you don't want to use the default SNC name |
|
|
|
SNC_PARTNERNAME |
SNC name of the SNC partner (RFC server) or SNC name of the message server (Load Balancing) |
|
|
|
SNC_QOP |
SNC Quality of service |
8 |
default (RFC_SNC_QOP_DEFAULT, see RFC_SNC_QOP) |
|
SYSNR |
SAP system number (R/3, No Load Balancing) |
|
|
|
TOUPPER |
conversion of user and password to upper case for sending to Web Application Server |
0 |
do not convert password to upper |
|
1 |
convert password to upper (default) |
||
|
TPHOST |
Host name of the external RFC server program |
|
|
|
TPNAME |
Path and name of the external RFC server program or Program ID of an registered RFC server program. |
|
|
|
TRACE |
RFC trace |
0 |
without trace (default) |
|
1 |
with trace |
||
|
TYPE |
RFC server type, 2/3/E: R/2 or R/3 or External System |
3 |
default |
|
USE_SAPGUI |
RFC with SAPGUI.
|
0 |
without SAPGUI (default) |
|
1 |
with SAPGUI |
||
|
2 |
invisible SAPGUI |
||
|
WAN_CONN |
RFC via Wide Area Network.
|
0 |
LAN (default) |
|
1 |
WLAN |
||
Alternative login possibilities:
|
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
ALIAS_USER |
An alias user name, could used instead of user or even together with USER. If both USER and ALIAS_USER are used, than they have to be match. |
|
EXTIDDATA |
Contains valid external user's ID of an external authentification system. User name is optional. External ID is to be defined in the backend (SAP-System). |
|
EXTIDTYPE |
Defines the kind of external identity. Valid only with EXTIDDATA. Follow values are not allowed: ID, NT; DN, CA, X, HX. Additionally, RFC Library provides the feature to retrieve MYSAPSSO2 certificate from the backend after successful logon. |
|
GETSSO2 |
Request to create a cookie version 2 using given password and user name. If the value is 1, the cookie will be generated from user and password values given by USER=user and PASSWORD=password in the same connect_param string. Instead, user and password X.509 certificate could be used. If the RfcOpenEx call ended successfully, the generated SAP cookie version 2 can be retrieved via RfcGetTicket API. |
|
MYSAPSSO |
SAP Cookie Version 1. Will be used instead of user and password for logon to backend |
|
MYSAPSSO2 |
SAP Cookie Version 2. Will be used instead of password for logon to backend. In this case, user name is optional. |
|
X509CERT |
An X.509 certificate will be used instead of password to logon to SAP System. In this case, user name is optional. |
