|
Syntax |
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
Semantics |
These macros do not work recursively and thus do not perform a deep copy of attributes of complex types. |
|
|
Substitutables |
|
Can be any complex object having attributes of any type. |
|
Examples |
|
|
Detailed Examples
Given are the two unrelated classes Person and DetailedPerson.
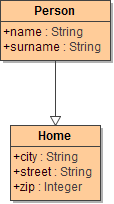
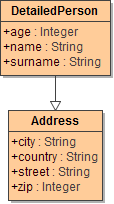
|
mapEqualNames() |
|
|---|---|
|
anInputPerson { age: 45, name: "Jane", surname: "Doe", city: "Los Angeles", country: "USA", street: "22, Main Road", zip: 90077 } |
The object |
|
|
This statement assigns values to the matching attributes of object
|
|
mapEqualNamesIfExists() |
|
|---|---|
|
aPerson { name: "John Ethan George", surname: "Smith", city: "New York", street: "65, Upper Eastside", zip: 0} |
The object |
|
anotherInputPerson { age: 32, name: "John", surname: "Smith", city: "New York", country: "USA", street: NULL, zip: 12345} |
The object |
|
|
This statement assigns values to the matching attributes of object
|
Usage of mapEqualNames() with append Statement
You can use the mapEqualNames()macro along with the append statement to add a complex object with numerous attributes to an array of unrelated objects which needs only some of the information. The mapEqualNames()macro will create set statements for all equal named attributes found in the target object while the append statement will add the result to an array.
Given are the two unrelated classes Person and DetailedPerson.

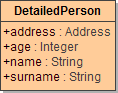
|
aDetailedPerson { adress: { city: "Los Angeles", country: "USA", street: "22, Main Road", zip: 90077 } age: 45, name: "Jane", surname: "Doe"} |
|
|
|
Result array:
|
