The following BPMN elements are supported for modeling in the Designer:
|
Page |
Element |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
With a Message Start Event you can start a BPMN model. "Message" is not restricted to emails or calls: Every action that represents or contains information for a recipient is a message. |
|
|
|
A Receive Task waits for an external trigger to arrive which is released by an external system. If the process execution reaches a receive task, the process stays in a wait state until a specific message is received by the engine, which triggers continuation of the process. |
|
|
|
The End Event marks the end of a process. If the process consists of several branches, all other open branches continue to run to their end. Every process branch needs its proper end event. |
|
|
|
A User Task waits for an external trigger to arrive which is released by human action, for example after a form has been filled. If the process execution reaches a user task, the process stays in a wait state until a specific message is received by the engine, which triggers continuation of the process. |
|
|
|
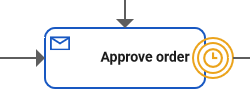
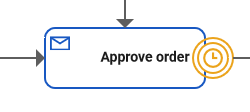
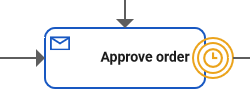
The Message Event waits for a message with a defined content. You can use the message event in the Designer as an intermediate event or as a boundary event:
Plain Event, Message Event and Timer Event can be used as boundary events along with User Task and Receive Task. When using the events as boundary events, attach the element directly to the border of the corresponding task: |
|
|
|
A Timer Start Event allows you to start a BPMN model after a defined cycle or at a defined time. Every time the timer is triggered, the model will be started. |
|
|
|
Timer Events are triggered by a defined timer. You can use the timer event in the Designer as an intermediate event or as a boundary event:
Plain Event, Message Event and Timer Event can be used as boundary events along with User Task and Receive Task. When using the events as boundary events, attach the element directly to the border of the corresponding task: To set the duration of the timer, the event should be trigged by a persisted property of type integer or datetime. You have two options to set the timeout in the attributes panel:
|
|
|
|
Use the lane element to design role-based processes. Assign one or multiple roles to a lane element and model all the steps that the assigned role(s) has/have to perform within that lane. |
|
|
|
Use a Start Event to start a BPMN model. |
|
|
|
The Imageelement enables the user to display a picture on the canvas, for example for documentation purposes. |
|
|
|
A Service Task is executed automatically when the process reaches it and the process continues to the next element when the execution ends. Use the execution pane to create the corresponding execution diagram defining the service task. |
|
|
|
The Free Text element allows the user to create an additional text field on the canvas, e.g. to display additional descriptions or notes. |
|
|
|
Use the Exclusive Gateway to model a decision in the process. The process will continue with the sequence flow where the defined condition is true. You can also define a default sequence flow (see Particularity).
|
|
|
|
The relation connects two objects. The direction of the arrow marks the process flow. Most relations are of regular type with the exception of outgoing flows of Exclusive Gateways.
|
|
|
|
The plain Event is able to catch signals. You can use the event in the Designer as an intermediate event or as a boundary event:
Plain Event, Message Event and Timer Event can be used as boundary events along with User Task and Receive Task. When using the events as boundary events, attach the element directly to the border of the corresponding task: |
|
|
|
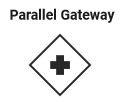
Use the Parallel Gateway to model concurrency in a process. You can use the object to fork the process. The functionality of the object is based on the incoming and outgoing process flows.
|