Provides utilities to deal with strings:
-
escape/unescape HTML, XML, JSON, CSV
-
calculate string distance (hamming, levenshtein, fuzzy) and sort arrays accordingly
-
substitute placeholders by values taken from a map
-
generate passwords obeying a number of criteria
-
generate random strings
-
generating UUIDs and ULIDs
-
encrypting/decrypting with AES
-
generic string utility operations
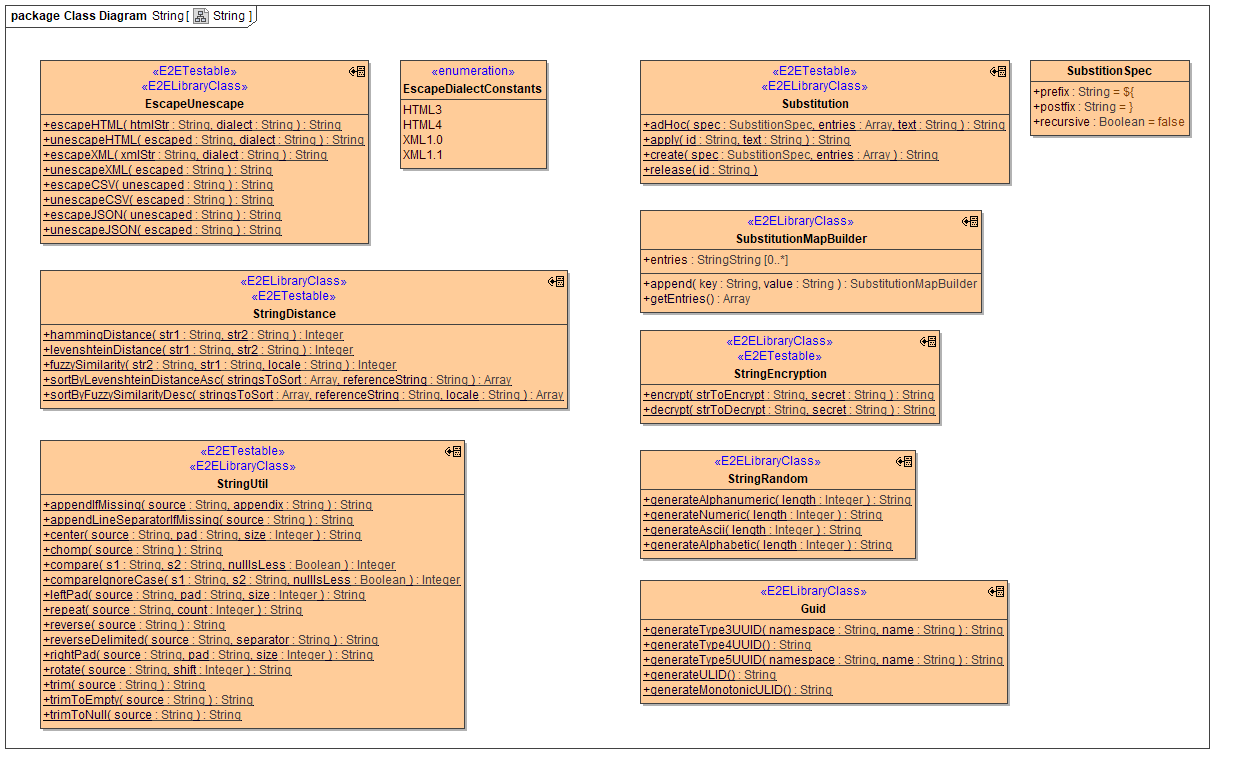
Escape and Unescape
This library class can be used to escape characters in strings for use as text elements in various formats, where these character have a special meaning. For HTML and XLM a dialect has to be specified, please use the most appropriate constant.
-
escapeXML('Wenn das Wörtchen wenn nicht wär, hätte ich > 1 Mio gewonnen.', 'XML1.0') = 'Wenn das Wörtchen wenn nicht wär, hätte ich > 1 Mio gewonnen.'
-
escapeHTML('Wenn das Wörtchen wenn nicht wär, hätte ich > 1 Mio gewonnen.', 'HTML4') = "Wenn das Wörtchen wenn nicht wär, hätte ich > 1 Mio gewonnen."
-
escapeJSON('values with "quotes", commas and \/ slashes') = 'values with \"quotes\", commas and \\\/ slashes'
-
escapeCSV('values with "quotes", commas and \/ slashes') = '"values with ""quotes"", commas and \/ slashes"'
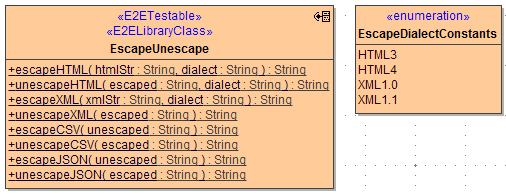
String Comparison
This class provides operations to compare Strings for distance, or similarity.
-
hammingDistance: compares to strings of equal length, and counts the number of positions where the string differ, i.e. the maximum distance is always the length of the strings.
-
levenshteinDistance: computes the "edit distance", i.e. what is the minimum number of character changes (insert, delete, or change) to make the first string equal to the second (or vice versa)
-
fuzzySimilarity: computes some similarity between two strings, where the "equalness" at the start weighs for more than at later positions
-
sort functions: given an array of String and a reference to compare to, generate a new array with the string sorted according to their distance/similarity to the reference
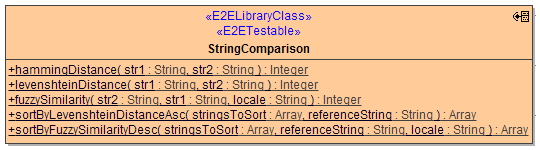
Substitution
This class allows for implementation of text templates which carry placeholders, that are then substituted by corresponding values provided in an array of map values.
-
there are two ways of using the functionality:
-
create a substitution, apply at several time, release it
-
carry out an ad hoc, or one-time, substitution
-
-
SubstitutionSpec
-
defines the pattern which surrounds a placeholder by prefix and postfix values (defaults to '${placeholder}')
-
defines whether recursive placeholders shall be resolved
-
-
entries array
-
defines the map between placeholder strings and actual values
-
an array entry is of type <<MapEntry>>StringString
-
think of it as e.g. [{'key1': 'value1'}, {'key2': 'value2'}]
-
Example ad hoc substitution


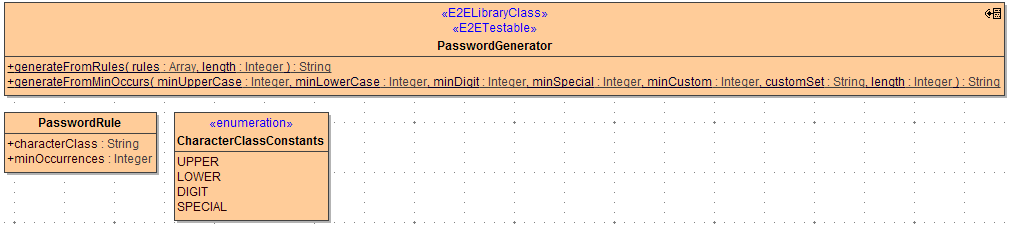
Password Generation
Use this class to generate passwords of a specified length that fulfill certain criteria.
-
criteria to be obeyed specify a class of characters and the minimum occurrences of characters from this class in the final password
-
character classes are:
-
UPPER: upper case letters
-
LOWER: lower case letters
-
DIGIT: digits
-
SPECIAL: special characters from the ASCII character set (one of: !"#$%&'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~)
-
CUSTOM: taken from a String you have to provide
-
-
-
generateFromRules
-
expects the criteria to be coded as an array of PasswordRule
-
specify the character class as either "UPPER", "LOWER", "DIGIT", "SPECIAL", or provide a custom string value to pick chars from
-
-
generateFromMinOccurs
-
expects the minimum occurrences of the various character classes as separate parameters
-
provide the custom character set as the customSet string parameter
-
-
values for minOccurrences <=0 will be ignored
-
values for minOccurrences that sum up to exceed the length parameter with throw an exception
Guide
This class allows to generate string representations of UUIDs (Globally Unique IDentifiers) as well as ULIDs (Universally Unique Lexicographically Sortable Identifier):
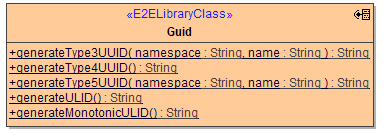
UUID
An UUID (most commonly referred to as GUID) is a globally unique 128-bit number, represented by a String of 36 characters with 5 groups from the hexadecimal alphabet separated by dashes in a 8-4-4-4-12 format, like this: 967a8cec-50fa-4acc-a1fe-5e29c4687bdb.
The library uses the java.util.UUID implementation for these.
Type-3 and type-5 UUIDs are generated by hashing a namespace identifier and name. Version 3 uses MD5 as the hashing algorithm, and version 5 uses SHA-1. Type-4 UUIDs are generated at random.
ULID
An ULID is a also a unique 128-bit number, represented as a String of 26 alphanumeric characters, like this: 01EWWZAR5FH0YTNYY63PHQD14D. A sequence of monotonic ULIDs is guaranteed to have a lexicographical sort order reflecting their time of creation.
More on that here: https://github.com/ulid/spec .
The library uses the ULID implemenation taken from here: https://github.com/huxi/sulky/blob/master/sulky-ulid/src/main/java/de/huxhorn/sulky/ulid/ULID.java
