Purpose
Use this if you receive date and time values as strings in an arbitrary but valid format, and you know the location where this is considered local time. The library parses the values and returns a DateTime object representing this date and time in UTC time. Daylight saving times are covered.
Usage
Java based operations most often require a time zone as parameter, as a String value. For a list of valid time zone strings see for example what-are-the-java-timezone-ids.
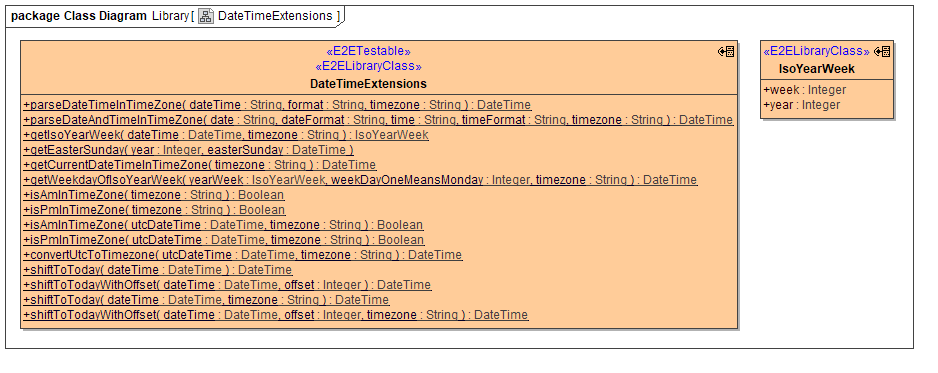
DateTimeExtensions
The library class DateTimeExtensions offers a couple of static operations (see class diagram below)
-
parseDateTimeInTimeZone()
-
dateTime: the DateTime to parse, e.g. "12.1.2017 6:30"
-
format: the format to use for parsing the DateTime, e.g. "%d.%m.%Y %H:%M"
-
timezone: the name of the time zone this date time comes from, e.g. "Europe/Zurich"
-
returns a DateTime object in UTC time representing the given date time input
e.g. "1.1.2016 6:30 Europe/Zurich" will return "01.01.2016T05:30:00Z", but "1.8.2016 6:30 Europe/Zurich" will return "01.08.2016T04:30:00Z"
-
-
parseDateAndTimeInTimeZone()
-
same as above, but expects the date and time portions separately, as well es the respective formats
-
convenience method in case you receive the strings separated, so you don't have to concatenate them first.
-
-
getIsoYearWeek()
-
dateTime: DateTime object in UTC
-
timezone: the name of the time zone this date time comes from, e.g. "Europe/Zurich"
-
returns an IsoYearWeek object covering the ISO week number and the respective year
e.g. 1.1.2016 will result in week 53 of 2015.
-
-
getEasterSunday()
-
no DateTime library is ever complete without an operation to calculate Easter for a given year
-
returns a UTC DateTime object at 0:00 AM on Easter Sunday
-
-
getCurrentDateTimeInTimeZone()
-
returns current date time as UTC DateTime for any given time zone, e.g. "Europe/Zurich"
-
-
getWeekdayOfIsoYearWeek()
-
yearWeek: instance of IsoYearWeek
-
weekDayOneMeansMonday: desired day of the week (1-7), where 1 means Monday
-
timezone: the name of the time zone for which to calculate, e.g. "Europe/Zurich"
-
returns beginning of that day (midnight) as UTC
-
-
isAmInTimeZone() and isPmInTimeZone()
-
returns true if the current time is AM or PM respectively (versions with timezone parameter only)
-
returns true if the given UTC time is AM or PM in the given timezone respectively (versions with utcDateTime and timezone parameter)
-
-
shiftToToday() and shiftToTodayWithOffset()
-
sets the date part of the given DateTime to today while preserving the time part, optionally shifting the result by "offset" days (versions with offset parameter, negative values allowed)
-
the versions with timezone parameter first translate all values to that timezone before calculating what "today" is (use these versions by default)
-
Date and Time Formatting
The date and time formatting (see above) allows for the same formats as defined in Date and Time Formatting, although internally this is converted to Java date and time formats. You can use Java date and time formats directly if you want.
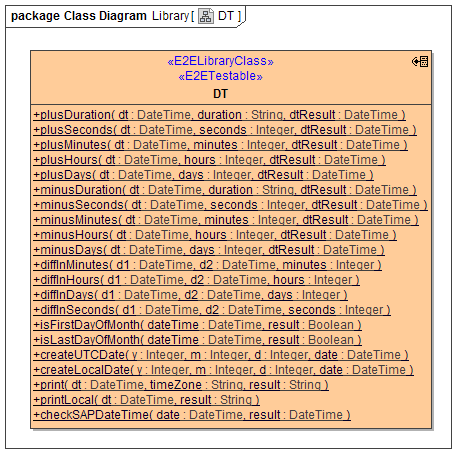
DT
DT class offers a variety of operations to add/subtract dates, calculate the distance (diff), check if a date is the fist or last of the month.
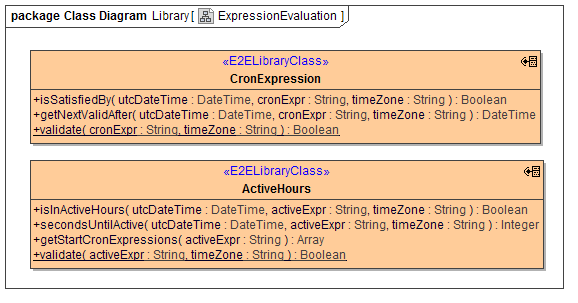
Expression Evaluation
Two classes are included to deal with expression evaluation.
-
CronExpression deals with cron expressions, like e.g. "0 10,44 14 ? 3 WED". The base Java implementation is from the Quartz Enterprise Job Scheduler and their tutorial describes very nicely what exactly is supported.
-
ActiveHours interprets expressions like e.g. "wd {Mon Wed Fri} hr {9am-4pm}, wd{Tue Thu} hr {9am-2pm}", i.e. comma separated expressions, each of which specifies a part of the week that is "active", i.e. business hours. The underlying Java code can be found on Github, which also features an extensive documentation of the supported syntax.
Important
"hr {9am-4pm}" actually means 9:00:00 to 16:59:59, or "after 9am and before 5pm".
All operations expect the time zone to consider (e.g. "Europe/Zurich").