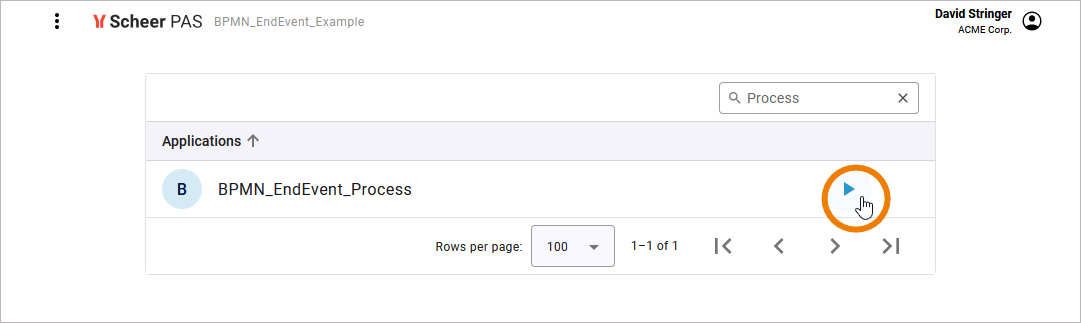
The Designer provides you with a role-based authorization concept (similar to the role-based authorization concept to run applications) that allows you to define which user is authorized to see the instance list of the respective process.
Each process has its own instance list. To access the role editor, select the respective BPMN model of your service on the diagram pane and switch to the attributes panel. Click Open role editor next to attribute Roles:
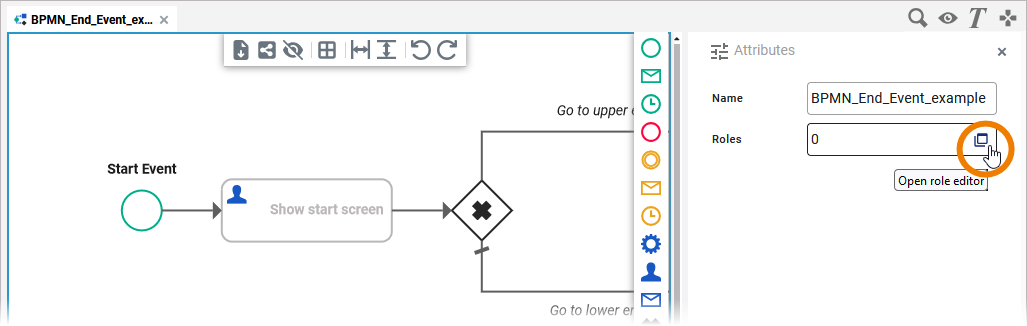
The role editor opens. The dialog initially contains an empty line to enter a role. The handling of the role editor is described in detail on Modeling Roles. There is one difference to the role editor of the instance list: For the instance list, you have no radio buttons to assign different rights to roles.
If no roles are assigned, the instance list is available for all users and a corresponding note is displayed.
The Role Concept in the Executed Application
Our example illustrates the usage of roles in the instance list. In the example, users David Stringer and Jane Marple have the following roles assigned:
|
Name |
Role |
|---|---|
|
David Stringer |
ACME Employee |
|
Jane Marple |
ACME Manager |
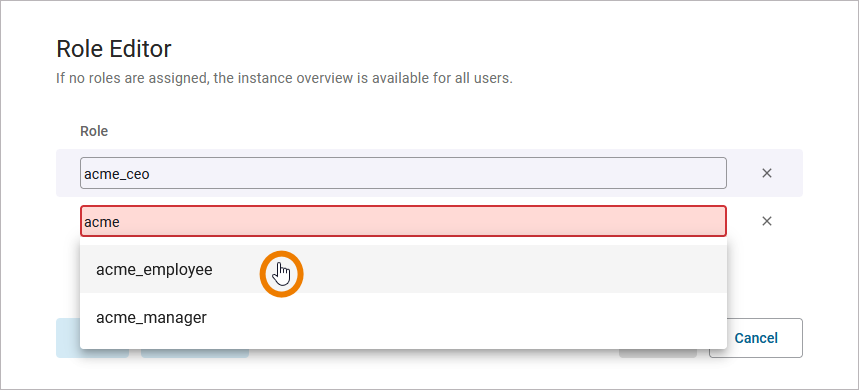
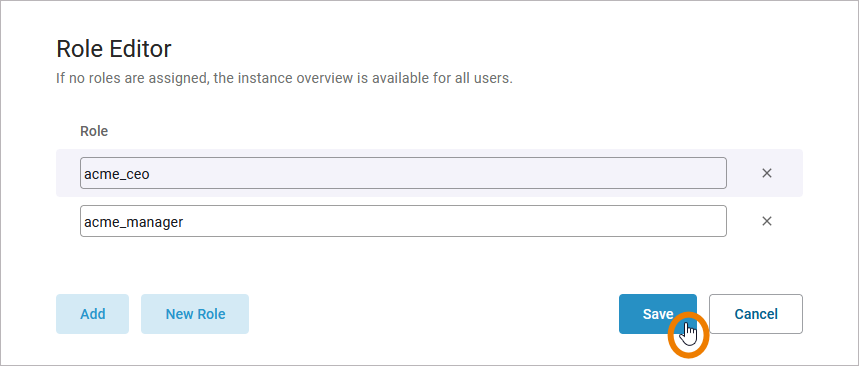
The following roles have the permission to see the instance list:
-
ACME Manager (acme_manager)
-
ACME CEO (acme_ceo)
Jane Marple has the role ACME Manager and thus has the necessary rights to see the instance list. On the application start page, she can see option Start to add a new instance (see Creating a Process Instance), and she is also able to click on the process row…
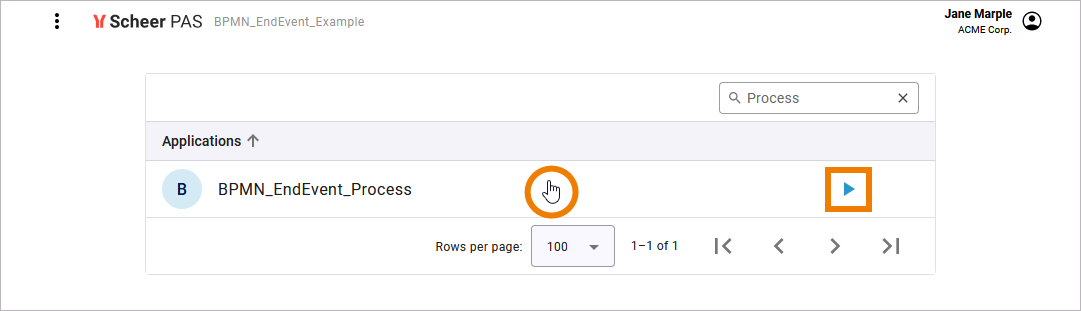
… which opens the instance list that displays all running instances:
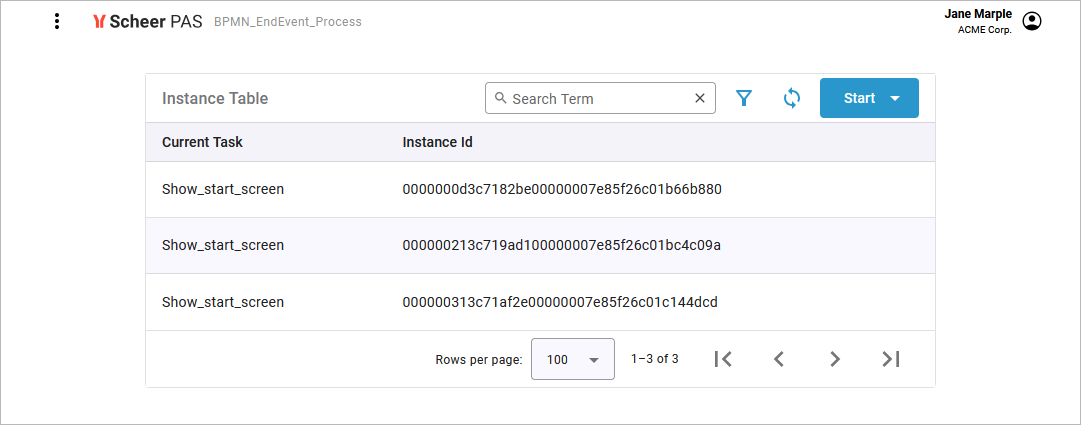
David Stringer is assigned the role ACME Employee. So he does not have the necessary rights to see the instance list. For him, clicking on the process has no effect, so he cannot access the instance list. On the application start page, he is only able to click option Start to create a new process instance: