In the Service Panel resides a folder API where you can define your own service APIs. In your service, go to the API folder in the service panel:
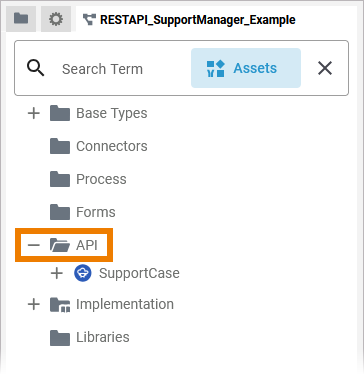
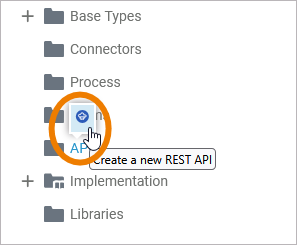
First you need to create the API needed for your service inside the API folder. All other elements will be created within this API. Create a new API via the quick action or the context menu. Refer to API for more information on how to create a new API in the API folder:
Expert Advice
Apply the same naming conventions to all your models. This makes reading a model much easier. Refer to Naming Conventions and Containment Tree Organization in the Builder User’s Guide for an overview on practice-approved naming conventions.
API Elements
To define a service API, you have the following elements available:
|
Element
|
Description |
Details |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
API
|
An API is the entrance port of your service. It can be used to communicate with the service from the outside. There are different kinds of APIs (e.g. REST API, SOAP API, ...) that describe different communication standards. |
||||||
|
|
Port |
Ports are elements of the UML modeling standard. A port defines an entrance point to the service and connects the API to an interface or class. |
|||||
|
|
Class |
A class is an aggregation of properties and operations that describes a complex data type from which objects can be created. |
|||||
|
|
Class
|
Classes can have sub-classes. |
|
||||
|
Operation |
An operation adds behavior to a class or interface. The behavior describes how to process the data given by the parameters. In the context of the Designer, you can implement operations as mapping diagram, activity, Action Script or JavaScript . |
||||||
|
|
Parameter |
Operations can have parameters that define the input and output objects. Operation parameters can be of simple type (Available Base Types) or of complex type (class or interface). |
|||||
|
Interface
|
In contrast to a class, an interface has no properties nor implementations. Interfaces are used to define common operations for multiple classes. In the deriving class, you must implement all interface operations. |
||||||
|
|
Interface
|
Interfaces can have sub-interfaces and sub-classes. |
|
||||
|
Class
|
|||||||
|
Operation
|
Operations and parameters for interfaces are the same as for classes. The difference is that they have no implementation but only define the signature for the dependent classes to derive from. |
||||||
|
|
Parameter |
||||||
Each element of the API folder has a context menu and quick actions. The context menu contains options to create new elements to the selected element, and to edit the current element. Via the quick actions, you can access the most used menu items directly with a single click.
API
An API is the entrance port of your service. It can be used to communicate with the service from the outside. There are different kinds of APIs (e.g. REST API, SOAP API, ...) that describe different communication standards.
The quick action of an API allows for the creation of ports:
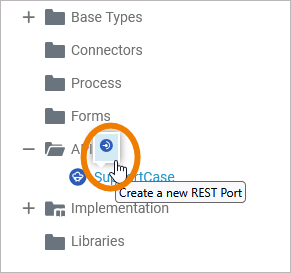
|
Quick Action |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Add a port to the API. |
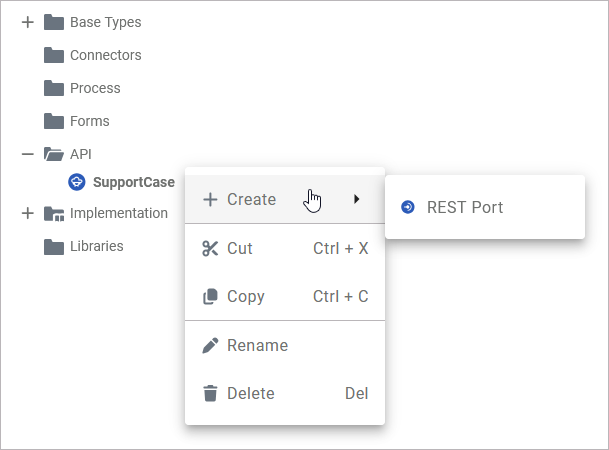
The context menu of an API allows you to create a port, to cut, copy and paste the API, to change the name of the API, and to delete it:
|
Menu Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Create > Port |
Add a port to the API |
|
Cut |
Cut the API to paste it elsewhere to the API folder. |
|
Copy
|
Copy the API to paste it elsewhere to the API folder. |
|
Paste
|
Paste the API elsewhere to the API folder. Available if Copy or Cut option have been used before. |
|
Rename
|
Change the API name. |
|
Delete
|
Delete the API. You can also use the Del or backspace key to delete the API element. |
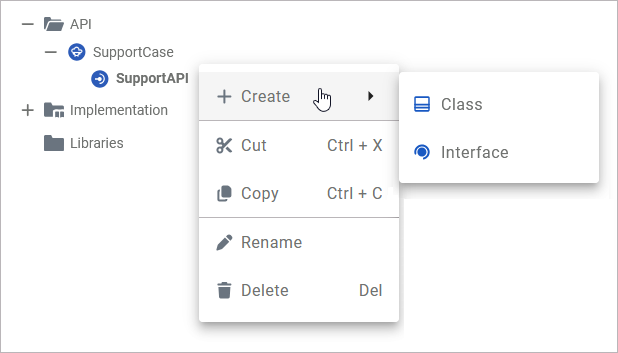
Port
Ports are elements of the UML modeling standard. A port defines an entrance point to the service and connects the API to an interface or class. The context menu of a port allows for the creation of classes and interfaces, to change the name of the port, and to delete it:
|
Menu Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Create |
Add further elements to the port. |
|
Cut |
Cut the port. |
|
Copy |
Copy the port. |
|
Rename |
Change the port name. |
|
Delete |
Delete the port. You can also use the Del or backspace key to delete the port element. |
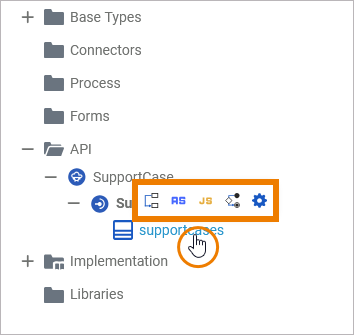
Class
A class is an aggregation of properties and operations that describes a complex data type from which objects can be created. The quick actions of a class allow for the creation of operations with different types of implementation:
|
Quick Action |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Add a mapping operation to the class. |
|
|
Add an action script operation to the class. |
|
|
Add a JavaScript operation to the class. |
|
|
Add an activity operation to the class. |
|
|
Add an operation to the class. The implementation is to be defined later. |
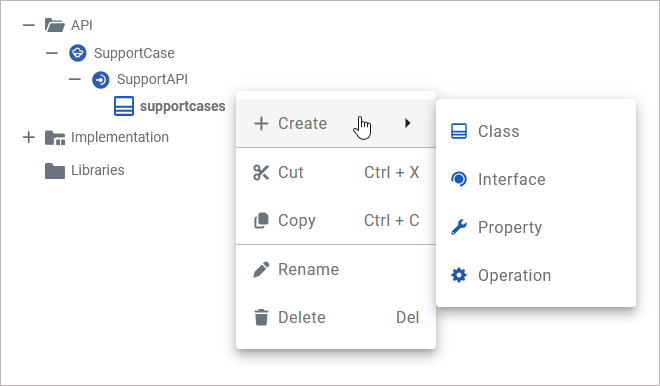
The context menu of a class allows you to create further elements, to cut, copy and paste the class, to change the name of the class, and to delete it:
|
Menu Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Create |
Add further elements to the class. |
|
Cut |
Cut the class to paste it elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. |
|
Copy |
Copy the class to paste it elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. |
|
Paste |
Paste the class elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. Available if Copy or Cut option have been used before. |
|
Rename |
Change the name of the class. |
|
Delete |
Delete the class. You can also use the Del or backspace key to delete the class. |
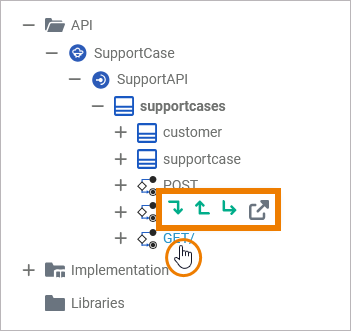
Operation
An operation adds behavior to a class or interface. The behavior describes how to process the data given by the parameters. In the context of the Designer, you can implement operations as mapping diagram, activity, Action Script or JavaScript .
The quick actions of an operation allow for the creation of parameters with different directions, and to jump to the implementation of the operation:
|
Quick Action |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Add an input parameter to the operation. |
|
|
Add an output parameter to the operation. |
|
|
Add a return parameter to the operation. |
|
|
Open the implementation of the operation in a separate tab. If you have not yet selected an implementation, a dialog opens first, which allows you to select the desired implementation. Refer to Create (Implementation) below for more information. |
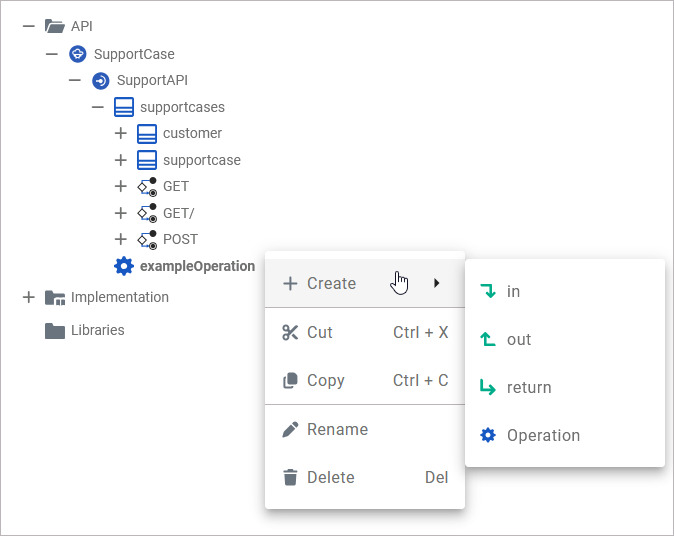
The context menu of an operation allows you to create further elements, to cut, copy and paste the operation, rename or delete the operation:
|
Menu Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Create > in |
Add an input parameter to the operation. |
|
Create > out |
Add an output parameter to the operation. |
|
Create > return |
Add a return parameter to the operation. |
|
Create > Operation (= Suboperation) |
Add a suboperation to the operation. |
|
Cut |
Cut the operation to paste it elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. |
|
Copy |
Copy the operation to paste it elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. |
|
Paste |
Paste the operation elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. Available if Copy or Cut option have been used before. |
|
Rename |
Change the name of the operation. |
|
Delete |
Delete the operation. You can also use the Del or backspace key to delete the operation. |
Parameter
Operations can have parameters that define the input and output objects. Operation parameters can be of simple type (Available Base Types) or of complex type (class or interface).
The context menu of a parameter allows you to change the order of parameters as well as to change the names of a parameter. Furthermore you can cut, copy and paste a parameter. It is not possible to create further elements below a parameter:
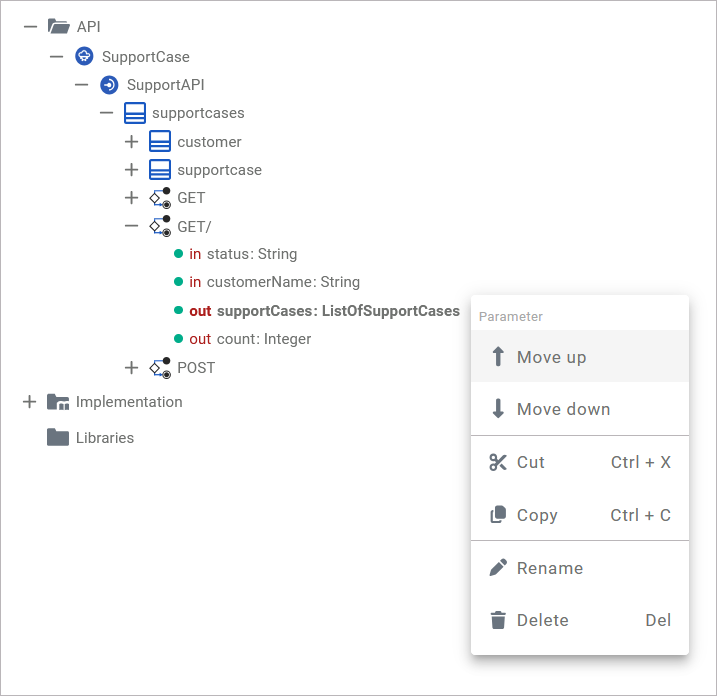
|
Menu Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Move up |
Change the order of parameters. |
|
Move down |
|
|
Cut |
Cut the parameter to paste it elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. |
|
Copy |
Copy the parameter to paste it elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. |
|
Paste |
Paste the parameter elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. Available if Copy or Cut option have been used before. |
|
Rename |
Change the name of the parameter. |
|
Delete |
Delete the parameter. You can also use the Del or backspace key to delete the parameter. |
If you want to change the direction of a parameter, select the parameter and change attribute Direction in the Attributes panel:
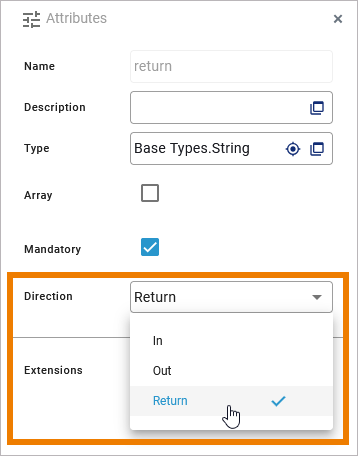
Interface
In contrast to a class, an interface has no properties nor implementations. Interfaces are used to define common operations for multiple classes. In the deriving class, you must implement all interface operations.
The quick action of an interface allows for the creation of operations:
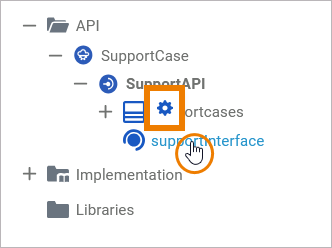
|
Quick Action |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Add an operation to the interface. Operations of interfaces have no implementation, they only describe the signature of the operation. |
The Interface context menu allows you to create further elements and to change the name of the interface. Furthermore you can cut, copy and paste as well as delete the interface via this menu:
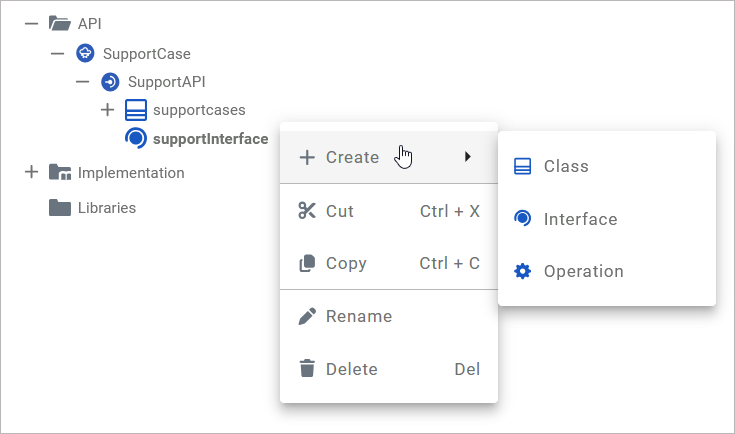
|
Menu Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Create > Class |
Add a class or subclass to the interface. Classes within interfaces can be nested. |
|
Create > Interface |
Add another interface to the interface. Interfaces can be nested. |
|
Create > Operation |
Add an operation to the interface. Operations of interfaces do not have an implementation but only define the signature (parameters and types). |
|
Cut |
Cut the interface to paste it elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. |
|
Copy |
Copy the interface to paste it elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. |
|
Paste |
Paste the interface elsewhere to the API or Implementation folder. Available if Copy or Cut option have been used before. |
|
Rename |
Change the name of the interface. |
|
Delete |
Delete the interface. You can also use the Del or backspace key to delete the interface. |
RESTAPI_SupportManager_Example
Click here to download a simple example model that shows the implementation of a REST API with Scheer PAS Designer.