- Created by Kirstin Seidel-Gebert, last modified by user-b5542 on Aug 29, 2022
You are viewing an old version of this page. View the current version.
Compare with Current View Page History
« Previous Version 7 Next »
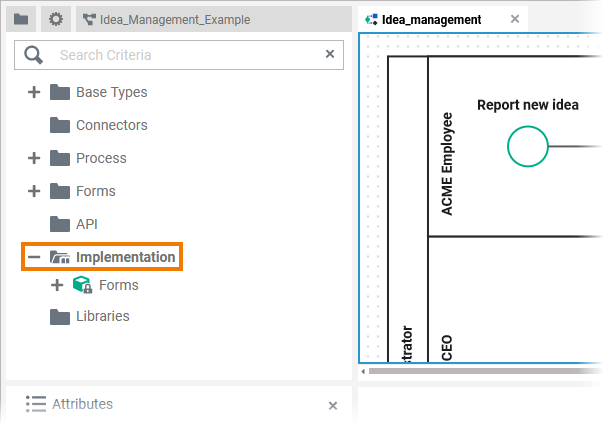
If you want to create your own data model within the Designer, you need to create a Service first. In the Service panel resides a folder Implementation where you can add your own data model to.
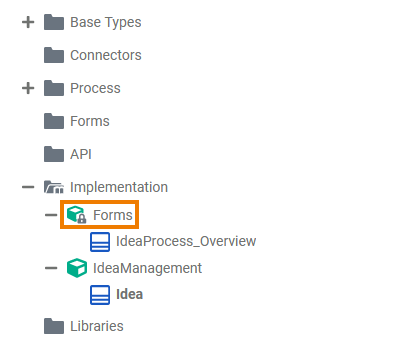
| Go to the Implementation folder in the service panel of your service. |
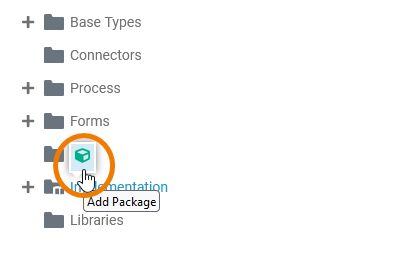
| All elements inside the Implementation folder need to be created within packages. Add a new package via the quick action or the context menu. Refer to Service Panel for more information on how to create elements in the service panel. Expert Advice Apply the same naming conventions to all your models. This makes reading a model much easier. Refer to Naming Conventions and Containment Tree Organization in the Builder User Guide for an overview on practice-approved naming conventions. |
Implementation Elements
To model your own data structures, you have the following elements available:
| Element | Description | Details | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Package |
A package is like a directory for the file system. It is used to group executable data model elements. Packages can have any depth of nesting: To structure your work, you can create packages within packages. | ||||
| Class | A class is an aggregation of properties and operations that describes a complex data type from which objects can be created. | ||||
| Property | Properties are data fields that describe the structure of the class. | ||||
| Operation | An operation adds behavior to a class or interface. The behavior describes how to process the data given by the parameters. In the context of the Designer, you can implement operations as mapping, action script or activity. | ||||
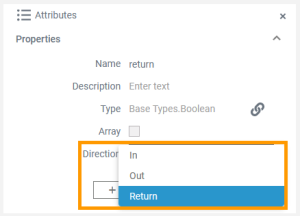
| Parameter | Operations can have parameters that define the input and output objects. Operation parameters can be of simple type (Base Types) or of complex type (class or interface). | ||||
| Interface |
In contrast to a class, an interface has no properties nor implementations. Interfaces are used to define common operations of multiple classes, and then derive from that interface. | ||||
| Interface | Interfaces can have sub-interfaces and sub-classes. | ||||
| Class | |||||
| Operation | Operations and parameters for interfaces are the same as for classes. The difference is that they have no implementation but only define the signature for the dependent classes to derive from. | ||||
| | Parameter | ||||
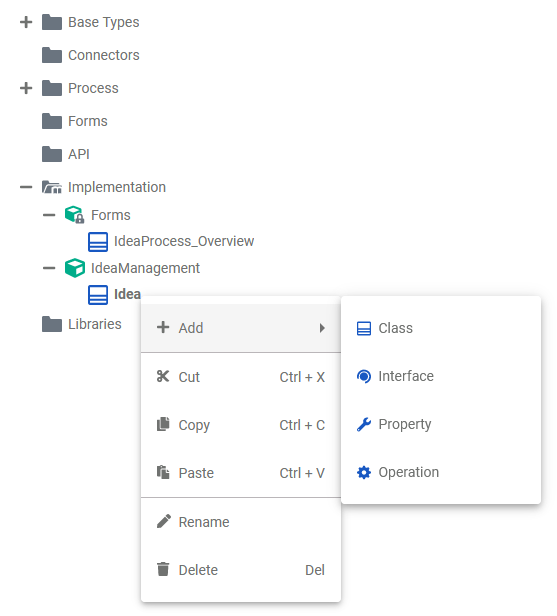
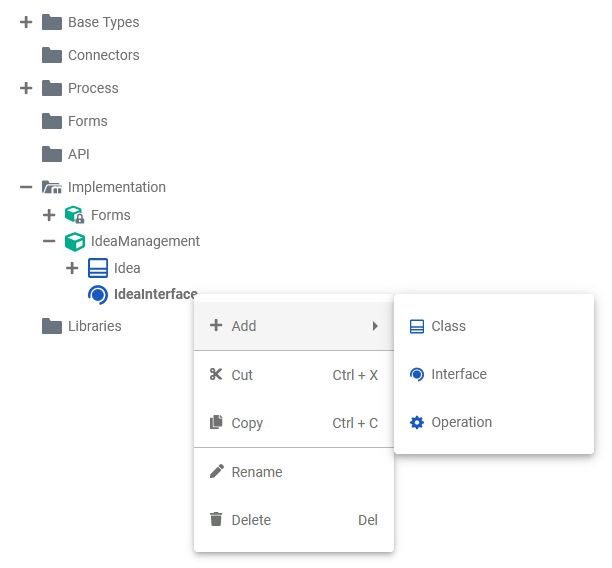
Each element of the Implementation folder has a context menu and quick actions. The context menu contains options to create new elements to the selected element, and to edit the current element. Via the quick actions, you can access the most used menu items directly with a single click.
Package
A package is like a directory for the file system. It is used to group executable data model elements. Packages can have any depth of nesting: To structure your work, you can create packages within packages.
Also, packages define a sort of namespace to the contained elements. The name of the package is part of the element path, e.g. Package1.Class is different from Package2.Class.
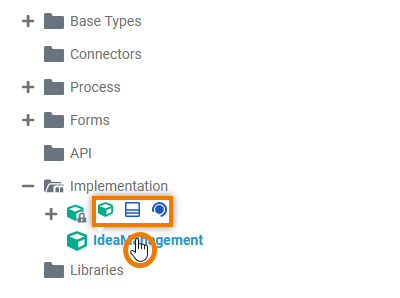
| The quick actions of a package allow for the creation of packages, classes and interfaces.
| ||||||||||||||||||
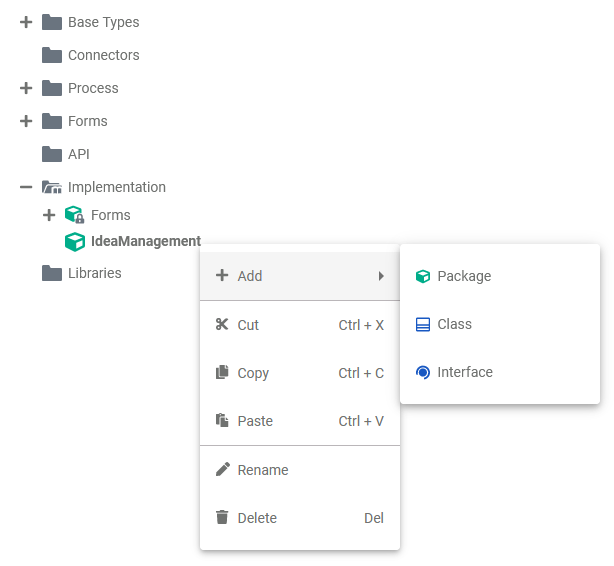
| The context menu of a package allows you to change the name of the package, and to create further elements.
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Package Message |
Class
A class is an aggregation of properties and operations that describes a complex data type from which objects can be created.
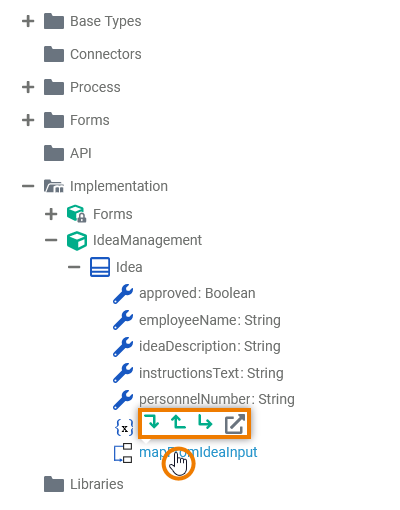
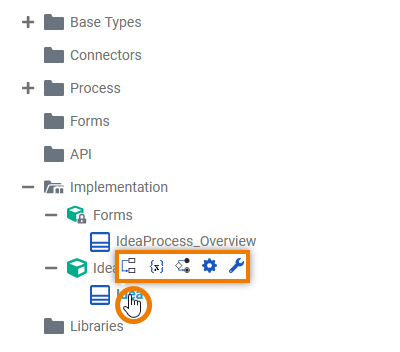 | The quick actions of a class allow for the creation of properties as well as operations with different types of implementation.
| ||||||||||||||||
| The context menu of a class allows you to change the name of the class, and to create further elements.
|
Property
Properties are data fields that describe the structure of the class.
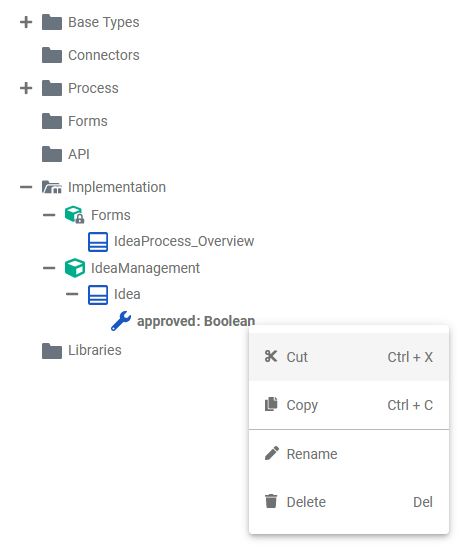
| The context menu of a property allows you to change the name of the property. It is not possible to create further elements below a property.
|
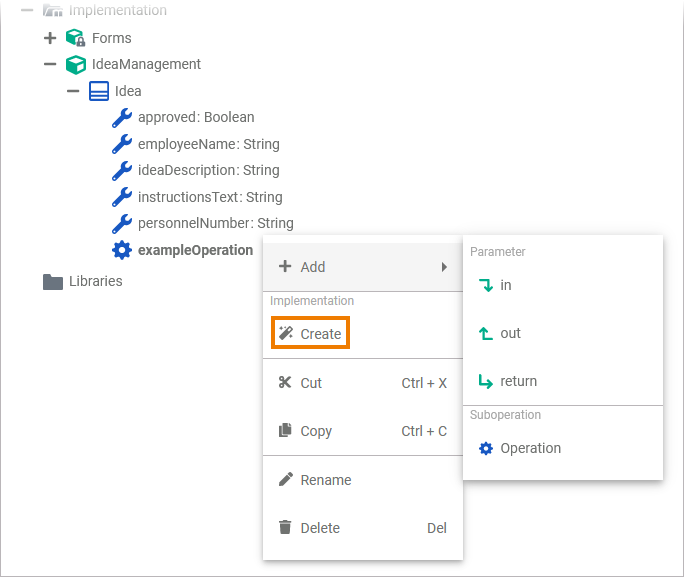
Operation
An operation adds behavior to a class or interface. The behavior describes how to process the data given by the parameters. In the context of the Designer, you can implement operations as mapping, action script or activity.
| The quick actions of an operation allow for the creation of parameters with different directions, and to jump to the implementation of the operation.
| ||||||||||||||||||
| The context menu of an operation allows you to change the name of the operation, and to create further elements.
|
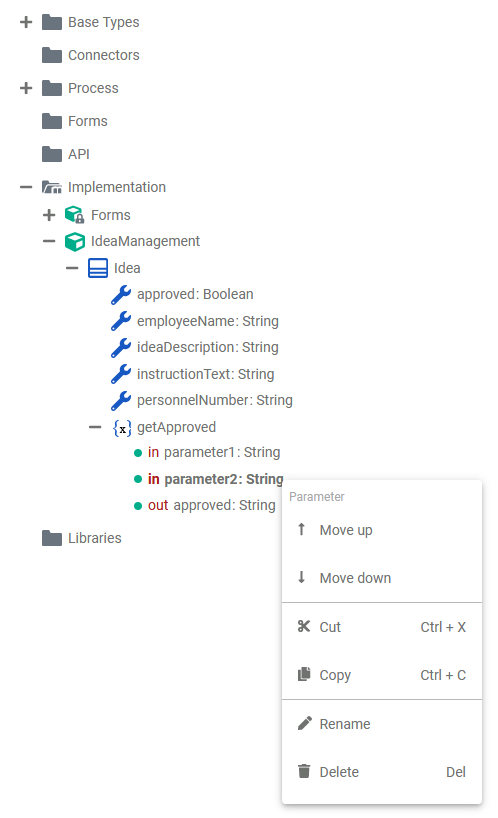
Parameter
Operations can have parameters that define the input and output objects. Operation parameters can be of simple type (Base Types) or of complex type (class or interface).
| The context menu of a parameter allows you to change the name of the parameter as well as to change the order of parameters. It is not possible to create further elements below a parameter.
|
Interface
In contrast to a class, an interface has no properties nor implementations. Interfaces are used to define common operations of multiple classes, and then derive from that interface.
Operations of interfaces do not have an implementation but only define the signature (parameters and types).
| The quick action of an interface allows for the creation of operations.
| ||||||||||||||||||
| The Interface context menu allows you to edit your interface and to create further elements.
|
- No labels