With BPMN, processes are started by start events. A process must have at least one start event, but it may also have multiple start events. During process start, a process instance is created.
Process instances are kept in the persistent state database: The instances are created on process start and deleted on process end. Refer to xUML Service State Machines for further information.
A process start is modeled by start events:
-
Start events will generate a POST operation to the API of the generated service.
-
This operation can be used to start an instance of the process within the service.
The Designer offers you several start events to choose from: Available Start Events.
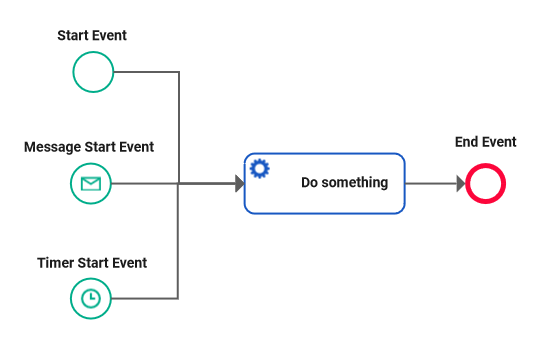
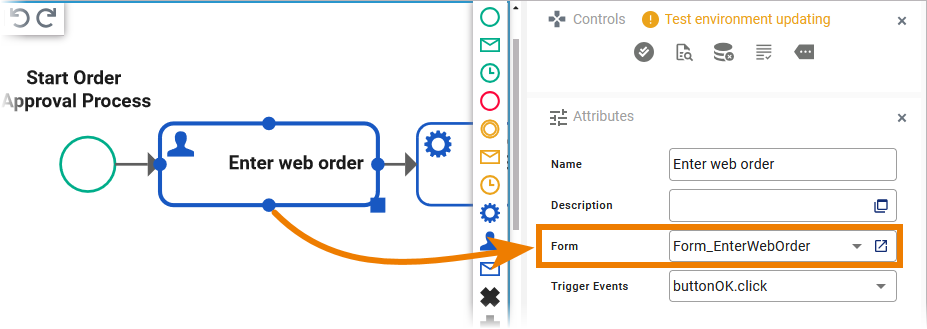
You can trigger the POST operation of a start event via the Angular application if your service contains at least one user task that has a form assigned:
After deployment, click Play to display all start events of the service. Select the one you want to use:
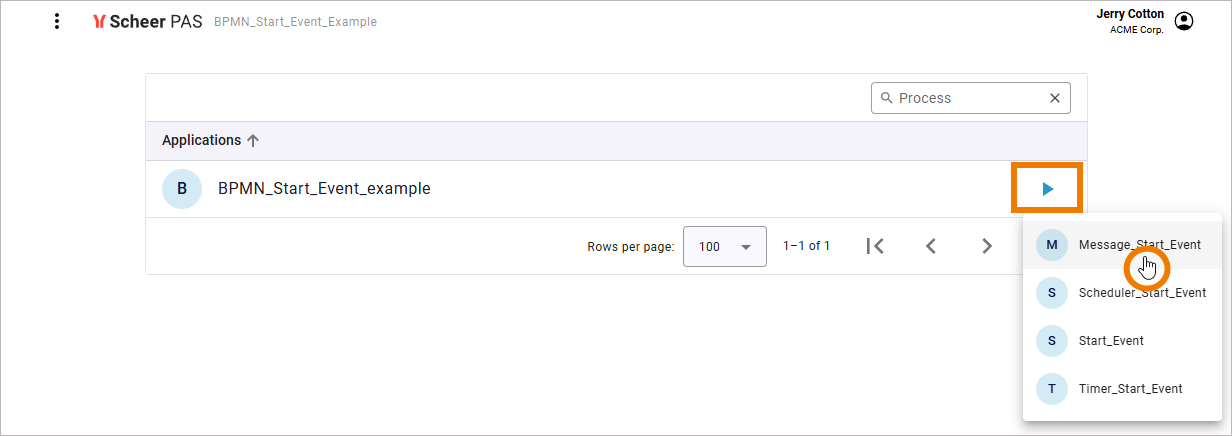
Refer to Deploying a Service for more information.
A start event can only be created via the elements toolbar.
Available start events are:
|
BPMN Element |
Usage |
Details |
|---|---|---|

|
|
See Start Event |

|
|
|

|
|
Start Event
The plain start event creates a process instance by a POST call (without parameters):

Refer to the reference page Start Event for all details.
You can create the execution model (On Event) for a start event:
-
The model will be executed when the start event occurs.
-
You can use this start event's execution model for preparations that need to be executed at the beginning of a process instance.
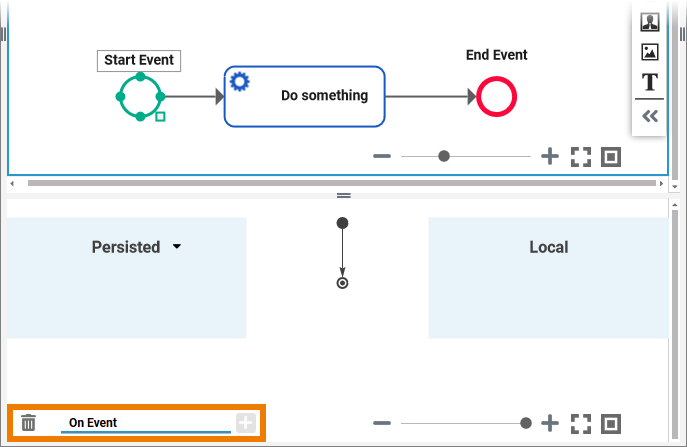
Message Start Event
"Message" is not restricted to emails or calls: Every action that represents or contains information for a recipient is a message. The message start event creates a process instance by a POST call (with parameters). The body of the POST call contains the defined message parameter.

Refer to the reference page Message Start Event for all details.
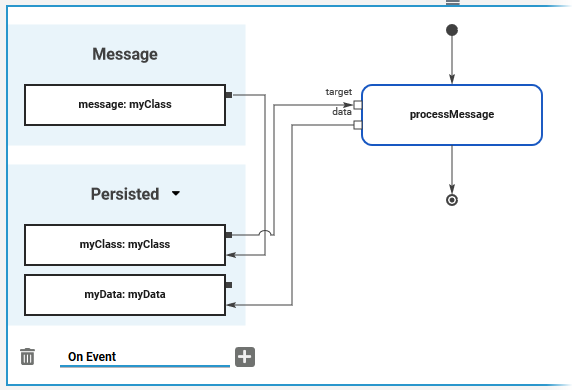
The execution model (On Event) for a message start event is created by default to process the message parameter:
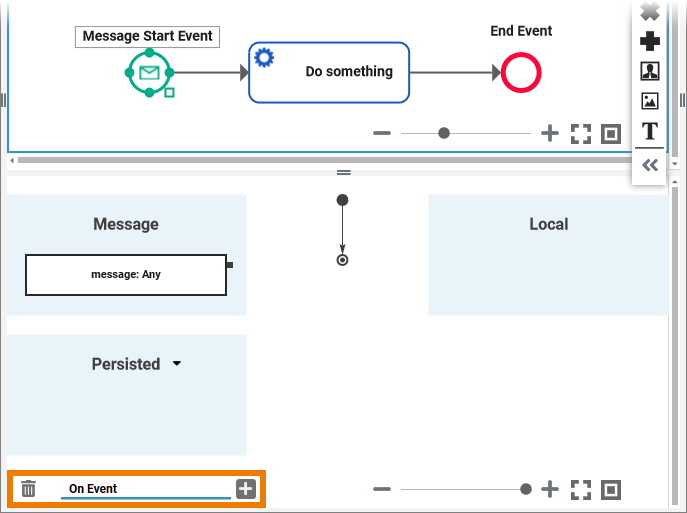
You need to define the type of the incoming message (replace any by a dedicated type):
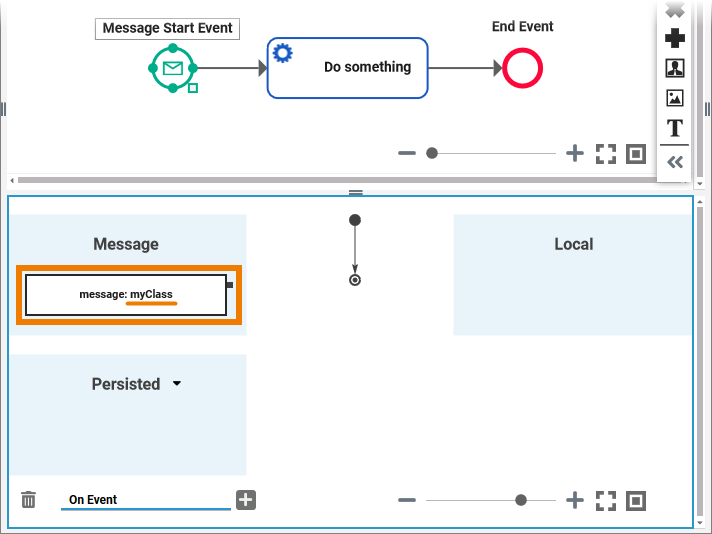
You need to at least persist the message parameter if you want to access this information later on in the process:
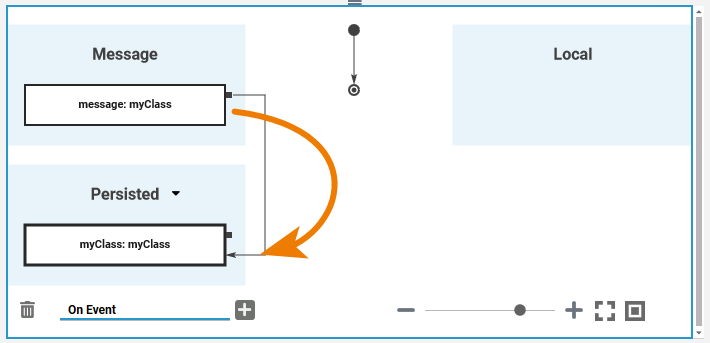
You can add more executional parts:
You can also remove the execution model. In this case, the message parameter is dropped:
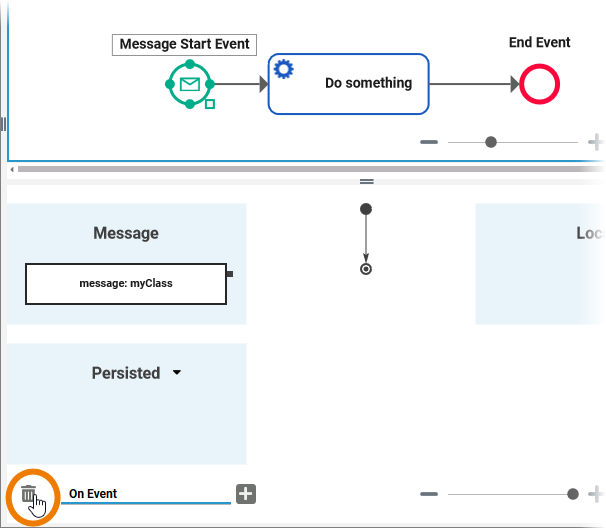
Deleting the execution model would only make sense in very special cases, e.g. if you do not need the parameter anymore but do not want to change the interface of the service. If you don't need the message parameter, use a plain start event instead.
Timer Start Event
The timer start event creates process instances based on time patterns (scheduler) or time cycles (timer). It is useful if you want to execute regularly recurring tasks:
Refer to the reference page Timer Start Event for all details.
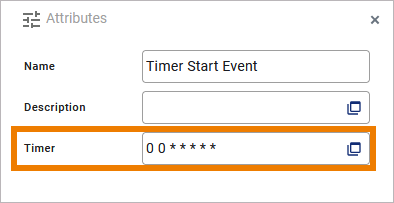
The generated service contains a timer or scheduler that triggers the process as defined. You can configure the timer/scheduler in the attributes of the timer start event, see Timer Start Event > How to Use the Scheduler/Timer for configuration details:
You cannot trigger the timer/scheduler from outside the service, it does not have a REST interface.
In your service model, you define the default of the timer/scheduler. If service requirements change, you don't have to change the model: You can change the timer/scheduler settings in the service configuration in the administration:
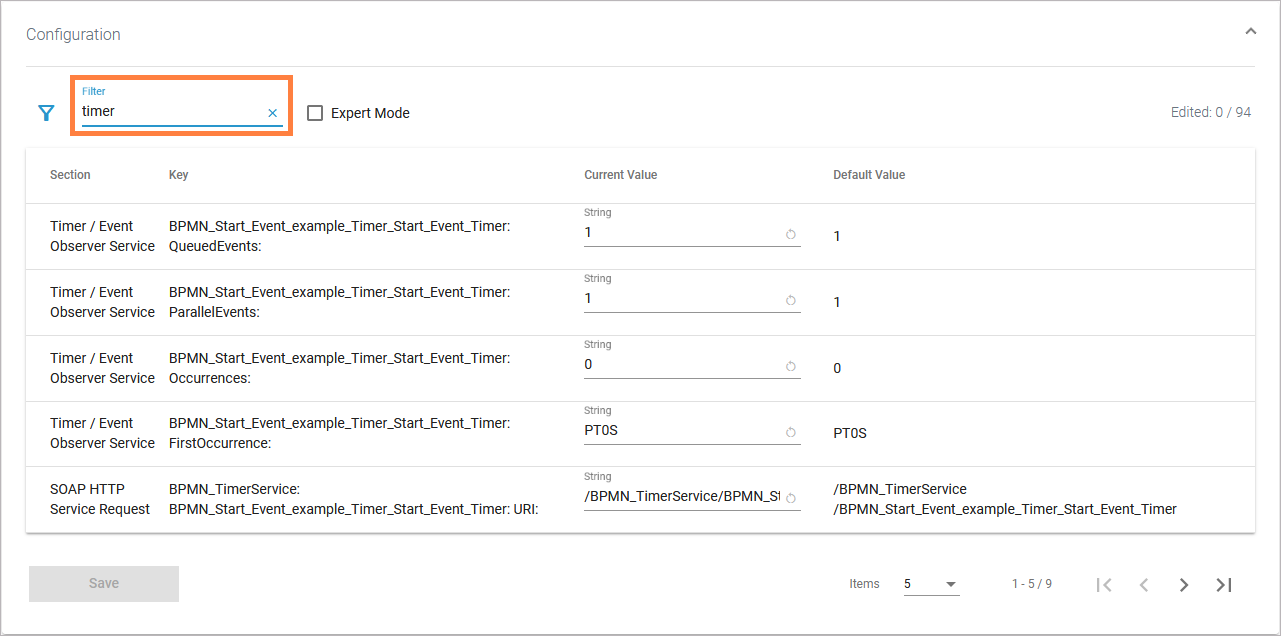
Depending on your PAS setup, refer to Adapting the Configuration of Containerized xUML Services (Docker) or Adapting the Configuration of Containerized xUML Services (Kubernetes) in the Administration Guide for details about how to change a service configuration.
You can create the execution model (On Event) for a timer start event. The model will be executed when the start event occurs.
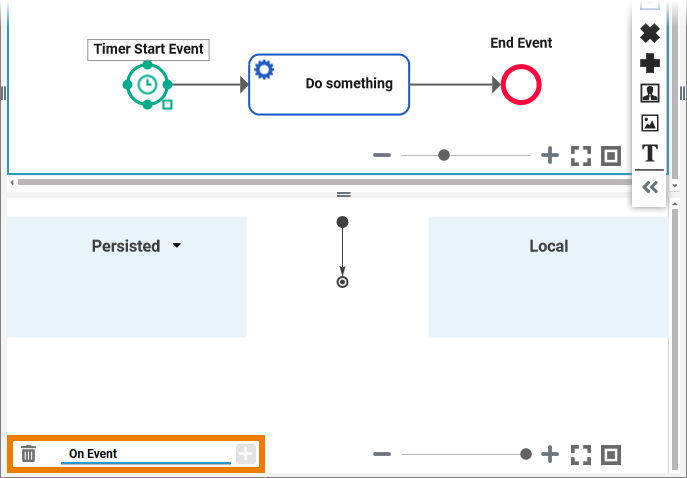
BPMN_StartEvent_Example
Click here to download a simple example model that shows what you can do with Start Events in Scheer PAS Designer.
