- Created by Annegret Bernhardt on Mar 30, 2022
You are viewing an old version of this page. View the current version.
Compare with Current View Page History
Version 1 Next »
This option is only available for type xuml-service (= containerized xUML services).
In the administration application you have the possibility to change the log level for a containerized xUML service.
You have two options to open the input form where you can change the log level:
| |
|
|
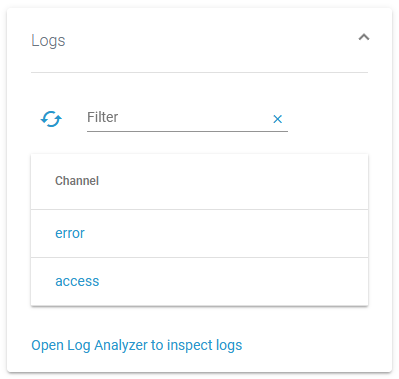
| The logging concept of the xUML Runtime is build around the concepts of channels and sinks. Refer to xUML Runtime Logger Configuration for detailed information. In sections Logs, you can choose between two channels:
The link below gives you direct access to the Log Analyzer, refer to Showing Logs of a Containerized xUML Service and Analyzing Platform Logs for further information. |
Select a channel to open the related channel sinks. Sinks define the logging output and how it is written. Refer to xUML Runtime Logger Configuration for detailed information. You can choose between two channel sinks:
| |
On the sink level, you can now adapt:
Please note that changes of the log level are directly applied to the container. They are effective until a restart or a recreation of the container which is also the case when the service settings are changed. | |
Use icon Click icon |
Log Levels of an xUML Service
The following server log levels can be set for each xUML service. The higher the log level the more information will be written to the log files. The log levels in the table below are cumulative and are ordered from the lowest to the highest log level. For each log level, also the information of the lower levels is logged.
| Log Level | Description |
|---|---|
| None | No logging will be executed. |
| Fatal | Fatal errors are logged. The component cannot continue with normal execution. Examples: repository errors, system limitations like no more available threads or memory. These errors need the intervention of an administrator to solve the problem. |
| Error | Also non-fatal errors are logged. If the UML modeler catches these errors, they are not written to the log. Examples are connection errors, wrong SQL statements, applying operations to invalid values, and so forth. Errors of this category are further classified:
|
| Warning | Warnings are logged. Warnings indicate unexpected but non-critical situations that do not interrupt normal operation. |
| Info | General information is logged. This includes, for instance, which component is being started or stopped, loaded add-ons, licensing information, etc. |
| Debug | In addition to log level Info, detailed trace information is written into an error file specified in the error message. Use this log level with care and only when investigating problems. As all tracing information has to be logged, it may result in significant loss of performance with increasing complexity of the deployed xUML service. |
If an error occurred, a call stack is written into the error log exposing the path to the action state where the error occurred in the model.[2006-04-20 08:31:13 W. Europe Standard Time][Error] [Internal][FUASM][3][Division by zero - Callstack: calculate > Calculation > call_Division > Division > Divide]
Transaction Log Levels
The following transaction log levels can be set for each xUML service. The higher the log level the more information will be written to the log files. The log levels in the table below are cumulative and are ordered from the lowest to the highest log level. For each log level, also the information of the lower levels is logged.
| Log Level | Description |
|---|---|
| NONE | No logging will be executed. |
| CUSTOM | Logs everything that is written by the logger adapter. |
| SERVICE | Logs the start and the end of calls to a service operation (service interface). For example, calls to SOAP, SAPRFC, or HTTP operations. |
| IO_EXTERNAL | Logs calls of adapters that communicate with external systems like SAP, SQL, SOAP, etc. For instance, the SQL queries that are sent to the database will be logged as well. Calls via the file system and system adapter are excluded. |
| IO_INTERNAL | Logs also calls of adapters to internal (local) resources (file system adapter and system adapter). |
Logging also includes start and end time of service calls and can be used to analyze process performance.
- No labels