Defining a REST API
Wanting to implement a REST API to a Designer service, you first have to figure out the resource structure. Have a look at the structure of the REST example:
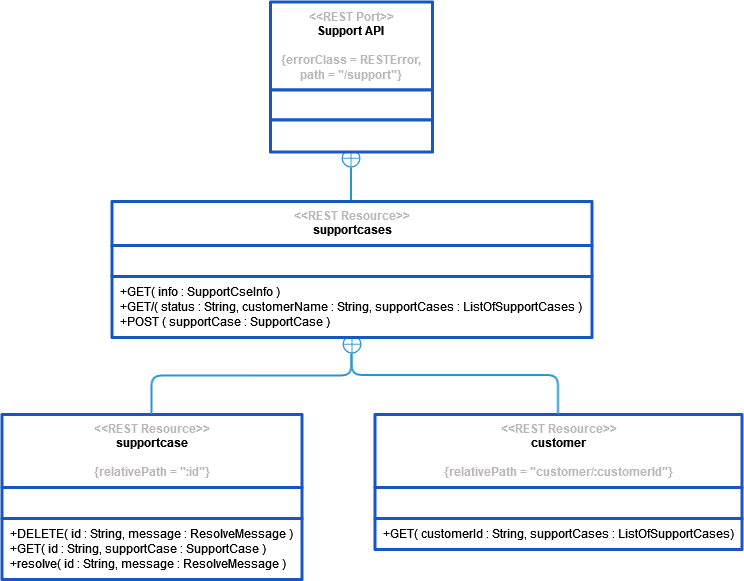
The rest interface SupportAPI has the following structure:
Resource | Methods | |
|---|---|---|
supportcases that accept GET, GET/ and POST. | GET | Get some information on the existing support cases. |
GET/ | Get all support cases. | |
POST | Create a new support case. | |
A single supportcase resource (below supportcases) that can be accessed via an id. | DELETE | Close a support case. |
GET | Get the data of a single support case. | |
GET | Set the status of the support case to "resolved". | |
A customer resource (below supportcases) that can be accessed via a customerID. | GET/ | Get all support cases of that specific customer. |
From the example, you can see implementations of GET, POST and DELETE methods. Of course, you can use the other available methods with the Designer, as there are PUT, PATCH, HEAD and OPTIONS.
REST resources are generated to the OpenAPI file with their class name only, instead of their fully qualified name (including the xUML package structure, like urn:Services.Classes.MyRESTResource). This implicates that their names have to be unique throughout the REST interface. The compiler will report an error, if it encounters REST resources having the same name in different packages.
You can add multiple REST APIs to a Designer service.
Defining a REST Port
Once you have created a REST API to your Designer service, you can add a REST port. A REST port is a class having the stereotype REST Port.
You can add multiple REST ports to the same REST API.
Example

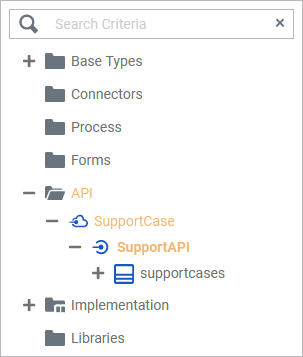
The REST port SupportAPI has path /support applied. The REST API can be accessed via /support instead of /API/SupportCase/SupportAPI as depicted in the service panel below:
The REST port has class RESTError applied as REST error class.
Defining Resources
A REST resource is a class having the stereotype REST Resource. This stereotype represents both: collections of resources (e.g. supportcases) and single resources (supportcase). Both are handled indifferently by the Designer. It is the modeler who should be aware, that some methods may not make sense on collections.
REST Resources have the following stereotype attributes:
Attribute | Description | Allowed Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
Relative Path | Defines the path of the REST resource or collection in relation to the parent resource. You can provide a static path, or a dynamic path using the notation | none | the name of the REST resource will be used, e.g. /supportcases |
any valid string | the given name will be used | ||
a dynamic path supplying a REST parameter | dynamic path, the value of the REST parameter will be passed to the REST methods, e.g. :id | ||
Is Verbatim Path | Disable most of the path normalization. All escaping must be done manually, leading or trailing whitespaces are preserved.
| true | Path should be treated as verbatim, path normalization is disabled. |
false (default) | Path should be URL encoded. | ||
Example
Example REST Resource | Description | |
|---|---|---|
supportcases |  | REST resource supportcases has no relative path applied. It will be accessible via |
supportcase |  | REST resource supportcase has a dynamic path applied: :id. The colon indicates that this path segment is a parameter. id must be a REST parameter and accepted by all REST operations related to this resource. For more information on REST parameters refer to Defining REST Parameters. |
customer |  | REST resource customer has a combined static and dynamic path applied: customer/:customerID. This is necessary to avoid conflicts with supportcase, which also has dynamic elements in its path. For more information on REST parameters refer to Defining REST Parameters. |
Defining REST Methods
A REST method is an method having the stereotype REST. REST methods must be static. With REST methods, we distinct between verb methods and named methods.
Verb Methods
Verb-methods intercept requests issued directly to the resource. Unlike named methods, verb-methods cannot specify path parameters other than the ones defined by the parent resource(s).
With the Designer, you can use all available HTTP methods, as there are GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, HEAD, and OPTIONS.
Example: AGETon /support/supportcases will route to the GET method of class supportcases and give an overview on the existing support cases.Named Methods
To call such method, append its name (or relativePath) to the parent resource.
Example: APUTon/support/supportcases/1234/resolvewill route to the resolve method of class supportcases.
The trailing /
Verb methods (unlike normal methods) can be in form of GET or GET/ - the difference is subtle but significant.
Think about the support manager example.
Issuing a
GETon/support/supportcases/is expected to return a list of existent support cases.A
GETon/support/supportcasesis expected to return information on the support cases in general, e.g number of support cases, list of customers afflicted, ...
REST methods have the following stereotype attributes:
Attribute | Description | Allowed Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
Http Method | Provide the HTTP method of this REST method should respond to. | a valid HTTP method | GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, HEAD, OPTIONS |
none |
| ||
Relative Path | Defines the path of the REST method in relation to the parent resource. | none | The name of the REST method will be used. |
any valid string | The given name will be used. The relative path may also contain variables (REST path parameters, specified as :<variable name>) and can be segmented like e.g. /date=:<a date variable> . | ||
Is Verbatim Path | Disable most of the path normalization. All escaping must be done manually, leading or trailing whitespaces are preserved.
| true | Path should be treated as verbatim, path normalization is disabled. |
false (default) | Path should be URL encoded. | ||
Blob Body Content Type | Specify a content type for Blob response parameters from this endpoint. This must be a valid "accept" header as defined in RFC 7231. This attribute must be left unset if no Blob output parameters are used. In future versions, the effect of this attribute may be extended to other contexts as well. | a list of valid media ranges | e.g. image/png |
Reject Other Response Content Types | The xUML Runtime performs a verification of the "accept" header for REST responses. Specify whether to return an error (HTTP 406, not acceptable) on requests with an "accept" header that does not conform with the content types specified in Blob Body Content Type. | true |
|
false | Accept the request in spite of the mismatch and handle this within the service. | ||
Accepted Request Content Types | Provide a list of content types this REST endpoint accepts. This must be a list of valid "accept" headers as defined in RFC 7231. This attribute must be left unset if no Blob output parameters are used. In future versions, the effect of this attribute may be extended to other contexts as well. | a list of valid media ranges | e.g. image/png;image/jpeg |
Reject Other Request Content Types | Specify whether to return an error on requests with a content type that does not conform with the content types specified in Accepted Request Content Type. | true |
|
false | Perform the adapter call in spite of the "content-type" header mismatch and handle this within the service. | ||
If the method name is one of GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, HEAD, OPTIONS (with optional trailing '/'), it will be invoked automatically on its parent resource when an corresponding request is received.
Examples
Example REST Resource | Method | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
 | GET and GET/ | verb method | Both methods have no httpMethod applied as GET is the default method. They will be invoked, when accessed via a |
POST | verb method | This method has httpMethod POST applied. It will be invoked on a | |
 | DELETE | verb method | This method has httpMethod DELETE applied. It will be invoked, when accessed via a |
GET | verb method | This method has no httpMethod applied as GET is the default method. It will be invoked, when accessed via a | |
resolve | named method | This method has httpMethod PUT applied. It will be invoked, when accessed via a | |
 | GET/ | verb method | This method has no httpMethod applied as GET is the default method. It will be invoked, when accessed via a |
Defining REST Parameters
A REST parameter is an input parameter of a REST method having the stereotype REST Parameter. This defines that this parameter will be provided via path, query, body, or header of the HTTP request. This has to be indicated on the parameter by setting stereotype attributes in:
Tagged Value | Description | Allowed Values | Allowed REST Methods | Allowed Types | Hints and Limitations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In | Defines how the parameter will be passed to the REST method. This tag is mandatory. | query | via a query string | all | all simple types and Array of simple type | Unknown parameters will be ignored, known will be passed to the method after being URL-decoded. |
path | via the REST resource path | all | Integer, Float, String, Boolean, DateTime | Path parameters are all required. All path parameters must be consumed by the called method and the parameter names must be the same as the path segment identifiers (without colon). | ||
body | via the REST call body | POST, PUT, PATCH | a complex type and Array | A REST method can have only one body parameter. | ||
header | via the REST call header | all | all simple types and Array of simple type | Unknown parameters will be ignored, known will be passed to the method. | ||
External Name | Defines an external name for the REST parameter. | any string | Use this, when wanting to access a REST service that has parameter names with special characters. In this case, set this name (e.g. | |||
All path parameters are required.
Examples
Example REST Resource | REST Parameter | Attribute "in" | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
 | status, customerName | query | status and customerName are provided via the query string: |
supportCase | body | For posting a new support case, the support case data supportCase is provided through the HTTP body. In this case, the xUML Runtime will automatically assign the data from the embodied JSON or XML document to the REST parameter class. | |
 | id | path | REST resource supportcase has a dynamic path :id applied. For this reason, all methods of this resource must have a REST parameter with the same name id that will receive the value from the URL. |
REST Errors
REST services in general return errors via the HTTP status code, so first of all, you should carefully choose the status code you are returning on a service call. Besides the HTTP status code there is no standard way of how to provide additional error information with standard REST service implementations. Developers can return additional information in HTTP headers or body, though.
With the Designer REST implementation, we decided to provide error information via the HTTP body by an error class or a Blob.
Each REST port type must have a default RESTError class assigned. The xUML Runtime will use this class as a default output in case of error.
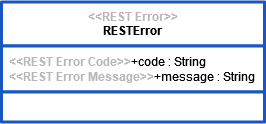
In case of error, this class should be
filled with some error information and
assigned to the REST HTTP response (so the error information will be returned to the caller)
The xUML Runtime will recognize attributes as error code and/or error message under the following conditions:
if you applied the names code and/or message to these attribute(s)
if you applied the stereotypes REST Error Code and/or REST Error Message to these attribute(s)
In this case, Runtime error codes and/or messages will automatically by assigned to these attributes in case of error.
Refer to Implementing REST Methods for more information on error handling.
Related Pages:
