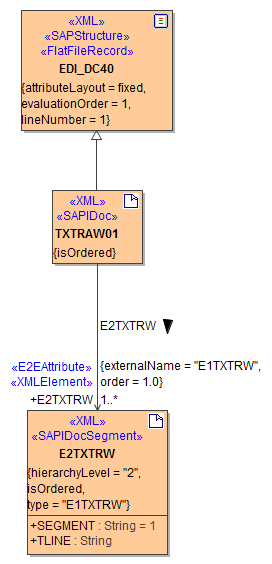
IDocs (Interface Documents) are modeled as UML classes (cf. TXTRAW01). Such classes can be serialized into SAP IDoc tables (arrays) by the <<SAPIDocRecordComposer>>.
There are two situations in which you may want to compose an IDoc data buffer:
You want to map an IDoc object (e.g. TXTRAW01, see figure below) to a SAP tables structure (mostly done, if you want to perform an SAP RFC).
This is done by an action having the stereotype <<SAPIDocRecordComposer>> (see Composing to SAP Tables).
After having composed an IDoc object, you can send it to an SAP backend using IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS. The necessary interface is already part of the base components. Refer to tRFC Service for more information on how to implement the call.
Figure: UML Class Model of IDoc TXTRAW01
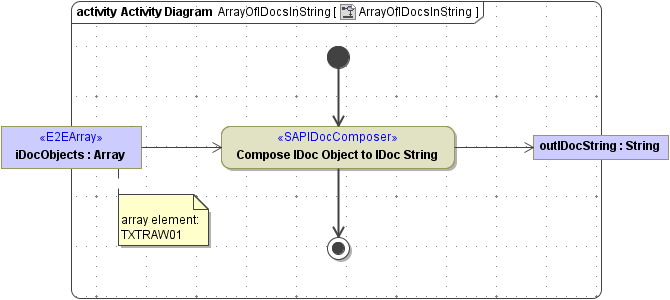
The <<SAPIDocComposer> takes one ore more IDoc objects as input and composes a String containing the object data. The structure of the data is kept (padding).
The following examples are demonstrating some applications of the <<SAPIDocComposer>>.
Figure: SAPIDocParser, Single IDoc to a String
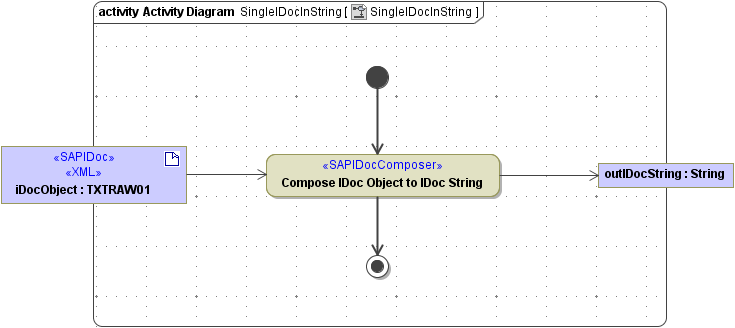
Figure: SAPIDocComposer, Multiple IDocs to a String
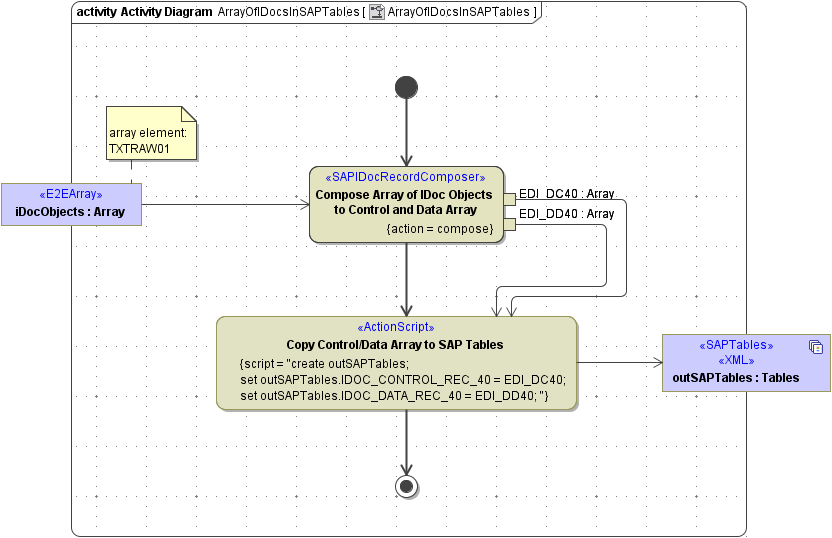
The <<SAPIDocRecordComposer> takes one ore more IDoc objects as input and composes an array of structured control records and an array of structured data records (as expected for SAP tables).
Figure: IDoc Composer with a IDoc-array to Tables
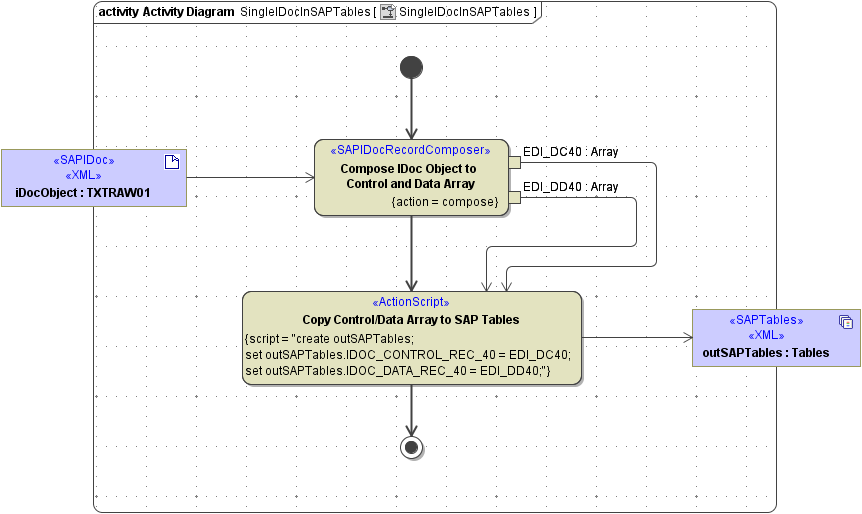
Figure: IDoc Composer with a IDoc-array to string
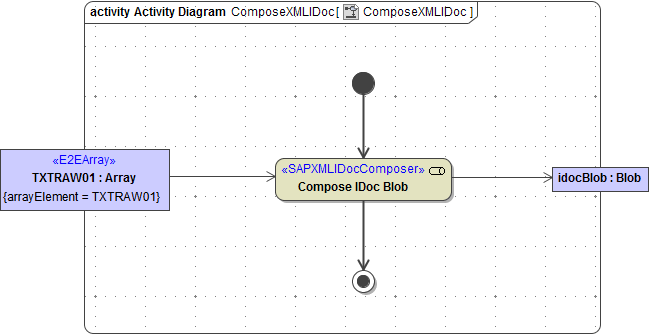
The <<SAPXMLIDocComposer> takes one ore more IDoc objects as input and composes a Blob containing the object data. The structure of the data is kept (padding).
The following example is demonstrating an application of the <<SAPXMLIDocComposer>>.
Figure: SAPIDocParser, Multiple IDocs to XML
The above examples show how to compose IDocs version of 4.x. However, SAP R/3 3.x systems use IDocs, too. These IDocs are handled similar as in version 4.x. The differences between composing version 4 and version 3 IDocs are as follows :