Parameters of Action "write"
| Name | Type | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | String | in | Fully qualified file name of the file you want to write, including the path. MultiExcerpt named hint_backslash_in_path was not found -- Please check the page name and MultiExcerpt name used in the MultiExcerpt-Include macro |
| position | Integer | in | Position (in Bytes) from which you want to start writing the file. |
| data | Blob | Content you want to write to the file. | |
| length | Integer | in | Length (in Bytes) of the data you want to write, if you want to only write part of the Blob. |
Defining a "write" Action
To write a file with the file system adapter, you need to define a write action on an action having the stereotype <<FileSystemAdapter>>. You can do this manually (refer to Figure: The Specification Dialog of the File System Adapter) or with the help of the E2E Action Wizard (see context menu of the action node).
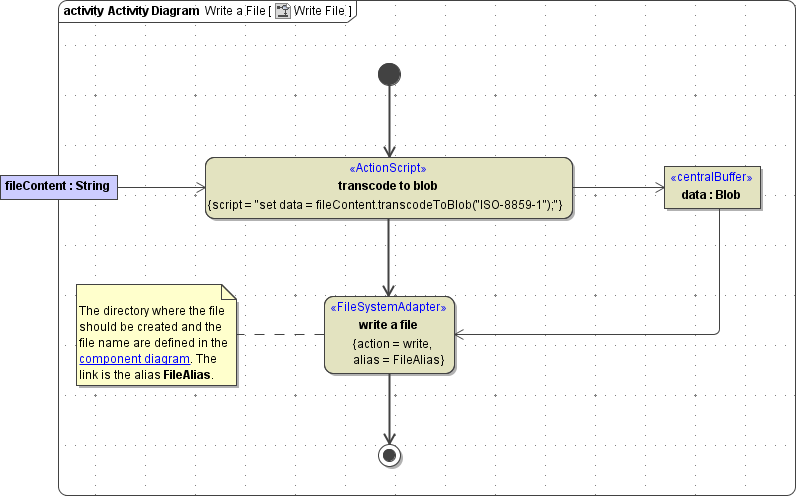
Figure: Writing a File
The file content needs to be provided as input of type Blob. The input object buffer must be named data.
The directory where the file should be created and the file name are defined in the component diagram. The link from the activity diagram to the physical information is established by an alias (in the present example: FileAlias). See File System Components for more information on file system aliases.
For information on how to access a file or directory dynamically refer to Dynamic File System Access.
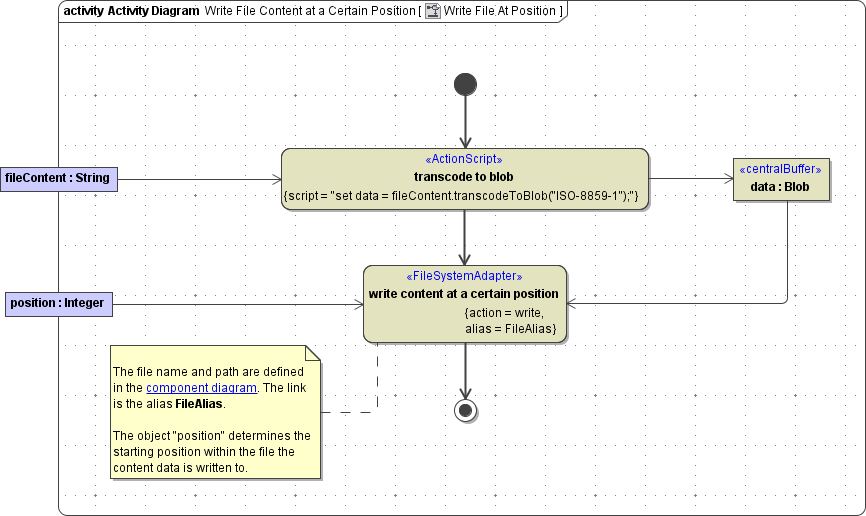
Writing Data to a Specified Position in a File
With the <<FileSystemAdapter>>, you can write data to a specified position within a file. You also need to define a write action (refer to Figure: The Specification Dialog of the File System Adapter). The only difference is, that you need to define a second input parameter. The parameter must be called position and is of type Integer. It defines the byte position within a file, at which the new content is written. Depending on the length of the new data, this will result in a partly update of the file content or an extension of the file. This can be useful when appending data to log files.
By retrieving the size of the file with the status action (see next chapter), you could easily append data to the file by determining the end position of the file and writing new content at this position.
Figure: Writing Data at a Specified Position