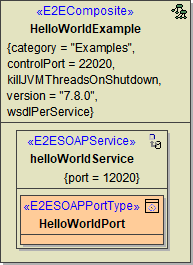
The most simple component diagram is depicted below. It contains a <<E2EComposite>> component. This component is the deployment unit of a set of service components. Each <<E2EComposite>> component may contain several services. The different service types are described in the Service Implementations section, e.g. SOAP, HTTP, JMS, Java, Timer, Scheduler, SAPRFC, etc. Finally, each service contains at least one class realizing the service. For example, SOAP services contain SOAP port types.
Figure: Component Diagram of the HelloWorldExample
Each composite manifests itself as repository file after compilation. This means, after compilation the <projectPath>/repository folder contains the repository file HelloWorldExample.rep. Additionally, each of the logical components can be configured by the use of tagged values. This repository belongs to the category E2E Examples and uses the control port 22020. For further composite attributes see the table below.
<<E2EComposite>> Attributes
The composite holds the following tagged values:
| Attribute | Type | Description | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | String | Name of the composite. | ||
| Category | String | Optional category to group similar xUML services. | ||
| ControlPort | Integer | Port used by the E2E Bridge to control this xUML service. | ||
| Version | String | A service version number. | ||
| Class To XML Default Root Name | String | Bridge 7 Specify which name to assign to the XML root element upon serializing. This setting can be overridden by using XML composer options as described on classToXML() Operation. Refer to XML - UML Class Mapping for more information on the topic of XML serialization. | Default | Try to use name and namespace defined on the class by the <<XML>> stereotype. Fallback to Variable Name if not provided (default). |
| Type Name | Use static name and namespace of the class as name of XML root element. | |||
| Variable Name | Use the name of the reference (object/variable) as name of XML root element. | |||
| JVM | ||||
| Read Modeling the Java Components for more information on these tagged values. | ||||
| Persistent State | ||||
| Read Persistent State Components for more information on these tagged values. | ||||
| SAP | ||||
| SAP Default Connection Pool Size | Integer | Default capacity of a single SAP connection pool (Bridge acting as a SAP client). If undefined, a default of 10 connections will be applied. You can override the connection pool size for a specific connection on the corresponding SAP alias. On using dynamic SAP access, the default connection pool size is used.
| default | 10 |
| SAP Padding | String |
Service-wide setting for SAP values padding. This setting will be applied to all IDoc and SAP adapters within the service.
| Never | No padding, removes existing padding (default). |
| Always | Always pad to specified length. | |||
| Mixed | Padding only fields that are not within deep structures. | |||
| SAP Server Worker Threads | Integer | Number of parallel request (workers) the Bridge (acting as an RFC server) can process. If this value is undefined, the Bridge will only process one request at a time (equivalent to sapServerWorkerThreads=1). Each worker consumes one license slot.
| default | 1 |
| Startup/Shutdown | ||||
| Startup Shutdown Trace Port | Integer | Default port for tracing startup or shutdown activities is 30000. you can change this default here, if necessary. | ||
| Startup Activity | Reference to Activity | The referenced activity is called while starting up before any other component gets invoked - including timers and schedulers. | ||
| Shutdown Activity | Reference to Activity | The referenced activity is called when the xUML Runtime is being shutdown. | ||
| Test | ||||
| Read Using Testable Classes for more information on these tagged values. | ||||
| WSDL | ||||
| WSDL Per Service | Boolean | If true (default=false), each xUML service gets its own WSDL file. Additionally, all XML Schema elements and types having the same namespace are put into one schema file. These schema files are imported into the WSDLs to be shared among them. In this case it is also possible to mix RPC/soap-encoded services with Document/literal services. | ||
| WSDL Namespace | String | Target WSDL namespace of the generated WSDL file. Relevant only, if wsdlPerService is false (this is the default). | ||
| Soap Version | String | Added in Builder 6.1 Specify the version of the SOAP protocol you want to use with the service. | 1.1 | SOAP version 1.1 (default) |
| 1.2 | SOAP version 1.2 | |||
| Resolve Inheritance | Boolean | If true, the inheritance hierarchy is resolved into flat messages. As of Bridge 7, setting resolveInheritance to true is deprecated, because this will generate a different output structure than modeled. It also has hidden requirements to the element uniqueness. | false | Keep inheritance hierarchy. (Bridge 7 default) |
| true | Resolve inheritance hierarchy into flat messages. (before Bridge 7 default) | |||
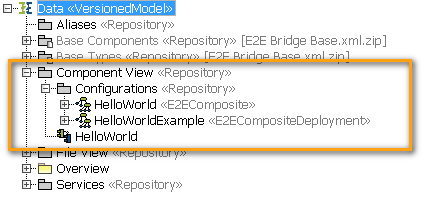
The component diagrams, the E2E composites, and services artifacts are always found in the same place in all E2E UML models:
Figure: Component View in the Containment Tree
Frontend Components of E2E Builder Version 5.1
- Deprecated since Builder 6.0