| Chapter | Name | Excerpt | Usage | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Array Operations | arrays_of_arrays | Arrays of arrays are not supported by the Designer. |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Array Operations | creating_arrays | You can create arrays using the create anArray; append "Hello World!" to anArray; Most of the time the xUML Runtime will create the array implicitly on appending the first item. There is one exception to this rule, though: Arrays that contain array elements having a complex type with multiplicity. Let's assume you have an array of complex type ArrayElement and this complex type has a property
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Blob Operations | blob_definition | A blob represents base64-encoded arbitrary binary data. |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| DateTime Operations | calculate_dates | This is calculated e.g. as follows:
| |||||||||||||||||||
| DateTime Operations | timeticks | Within this context TimeTicks are UNIX timestamps. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Integer Operations | boolean_definition | Boolean values represent binary-valued logic (true, false). |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Integer Operations | datetime_definition |
Whereas "Z" stands for the time zone: Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The W3C value space of DateTime is closely related to the dates and times described in ISO 8601. |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Integer Operations | float_definition | A float corresponds to the IEEE single-precision 32-bit floating-point type. Lexical representation: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Integer Operations | integer_definition | The W3C defines integers as "decimal", which represents arbitrary precision decimal numbers. |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Integer Operations | string_definition | A string is a set of finite-length sequences of a character set (the Bridge uses UTF-8 internally). |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| JSON | writeTypeDiscriminator | Use writeTypeDiscriminator to suppress the generation of xUML type properties ("e2e:type") to the generated JSON. If this option is true, the Runtime will write the original xUML type to the generated JSON in form of | |||||||||||||||||||
| Types | list_type_strings | Find below a list of all Base Types of the Designer together with their type string as returned by
Other, e.g. model specific, types can be referenced via their path in the service panel, e.g. a class Customer that has been defined in a package Service/Classes/Customer would have the following type string: " urn:Service.Classes.Customer ". | |||||||||||||||||||
| XML Mapping | classToXML_mapping_rules | By default the following mapping rules apply:
These default rules can be overridden by stereotypes (XML, XMLNamespace, XMLElement, XMLAttribute, XMLCharacters) on class attributes. | |||||||||||||||||||
| XML Mapping | classToXML_mapping_rules | By default the following mapping rules apply:
These default rules can be overridden by stereotypes (X) on class attributes. | |||||||||||||||||||
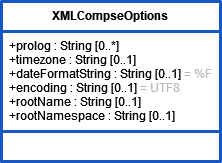
| XML Mapping | classToXML_options | This optional parameter is an object of type XMLComposeOptions. Its attributes are: |