Page History
| Div | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
|
The most common use case for tRFC servers is receiving IDocs from SAP. The tRFC server example implements an xUML service that makes the Bridge acting as a tRFC server and shows how to receive IDocs from SAP.
...
The transaction handling is separated from the actual exchange of data and must be handled by implementing all of the following callback operations:
| Callback Operation | Description | Return Value |
|---|
| onCheckTID | This function will be activated, if a transactional RFC is called from an SAP system. The current TID (Transaction ID) has been handed over to the function.
| 0 | ok |
| not 0 | TID already in use | ||
| onCommit | This function is called, if all RFC functions belonging to this transaction are done and the local transaction can be completed. It should be used to locally commit the transaction, if working with database. | ||
| onRollback | This function is called instead of onCommit, if an error occurred in the RFC library while processing the local transaction. This function can be used to roll back the local transaction (working with database). | ||
| onConfirmTID | This function is called, if the local transaction is completed. All information about this TID can be deleted. | ||
Implementing tRFC Operations
...
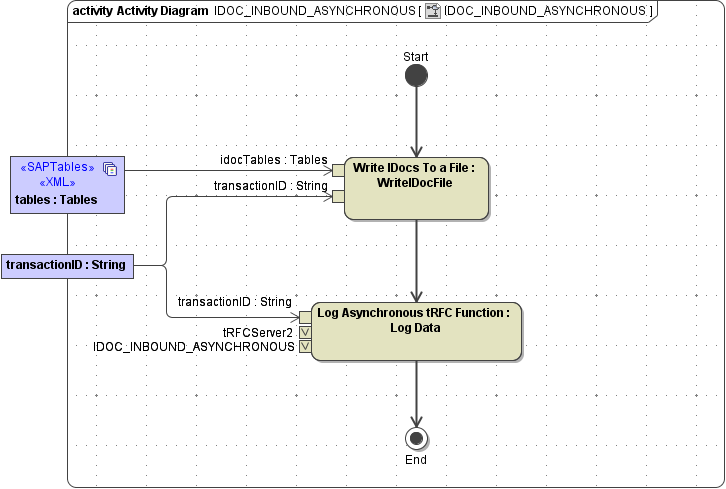
Figure: IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS
| Noteinfo | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Only inbound data flow is allowed for SAP tRFC functions. That is tables and importing parameters. Additionally, when implementing a tRFC function, the modeler can access the current transaction ID via the transactionID input parameter. |
tRFC Service Components
...
| SingleLine | false |
|---|
...
Builder 6
...
Each <<E2ESAPRFCService>> that uses tRFC contains at least two residents:
...
| Multiexcerpt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noteinfo | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
|
...
The program ID must be defined on the SAP system in transaction SM59. This transaction enables the user to define TCP/IP connections (connection type T). Each such connection has an associated program ID that must be exactly the same string as used for the tagged value programID on the <<E2ESAPRFCService>> component. Note, that this string is case sensitive. On the <<E2ESAPRFCService>> component, you also specify the port number of the SAP gateway the server registers on.
| Noteinfo | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
The Model Compiler throws an error, if a composite service contains more than one <<E2ESAPRFCService>> component. This constraint is given by the very nature of a SAP gateway. Each operating system process must register exactly one program ID at the gateway, otherwise the dispatching of SAP requests to the RFC service is not unique. Now, each xUML service runs in its own Bridge process, thus unique dispatching can only be achieved by allowing only one RFC service - i.e. one program ID - per xUML service. |
tRFC Service Components of
...
Builder Version 5.1
...
Deprecated since Builder 6.0
| Expand | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
Each <<E2ESAPRFCService>> that utilizes tRFC contains at least two residents: One and only one <<E2ESAPTRFCCallbacks>> class holding operations to control transactional behavior (for instance the TRXLogging class beneath) and one or more <<E2ESAPRFCModule>> classes containing operations called by the SAP system to exchange data. For instance, see the IDocInterface class depicted in the deployment diagram beneath. The implementation of these operations is similar to the implementation of standard RFC operations. The only difference results from the asynchronous nature of tRFC operations - they handle input only. Figure: tRFC Service Component Diagram The components are manifested by their artifacts, which instantiating the components and annotating all configuration information to run these components on their target systems. The tRFCServiceDeployment has the following tagged values:
Basically, tRFC server components must be registered at the so-called SAP gateway. For example, the artifact tRFCServiceDeployment is registered at the gateway-artifact sapgw00 via the program ID E2E_RFC_ZERTIFI_SERVER_ID. The program ID must be defined on the SAP system in transaction SM59. This transaction enables the user to define TCP/IP connections (connection type T). Each such connection has an associated program ID that must be exactly the same string as used for the tagged value programID on the <<Register>> dependency. Note, that this string is case sensitive. The <<Register>> dependency points to a component artifact having the name of the SAP gateway the server registers on. This name is given by: sapgw + system number of the SAP system.
|