- Created by user-b5542, last modified by Annegret Bernhardt on Jan 05, 2024
| Syntax | set aBlob = anObject.classToXML() set aBlob = anObject.classToXML(options) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semantics | The operation takes any object ( By default the following mapping rules apply: These default rules can be overridden by using the stereotypes XMLElement, XMLAttribute, and XMLCharacters on class properties. A conversion with operation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substitutables | anObject | Target object can be any complex object. However, simple types and arrays are not supported, since they do not map naturally to a well formed XML document. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
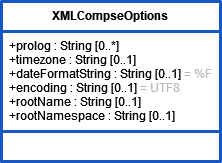
options |
Its attributes are:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Examples | set xmlBlob = myAddress.classToXML(); | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
XML Serialization Example
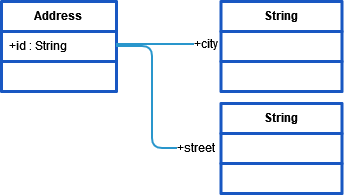
Assume you have an object myAddress of type Address .
The following action script serializes this object.
set xmlBlob = myAddress.classToXML();
The sample XML document below illustrates the mapping executed by classToXML(). The object myAddress of type Address is mapped to an XML document as depicted in the following XML document:
<myAddress id="myAddressID">
<street>108, Kearny Avenue</street>
<city>Newark</city>
</myAddress>
Note, that the XML element myAddress is of type Address . This type has the attribute id, which corresponds to the XML attribute id. Additionally, the XML elements street and city are mapped to the association ends city respectively street. Both are having the type String.