Page History
| Div | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
|
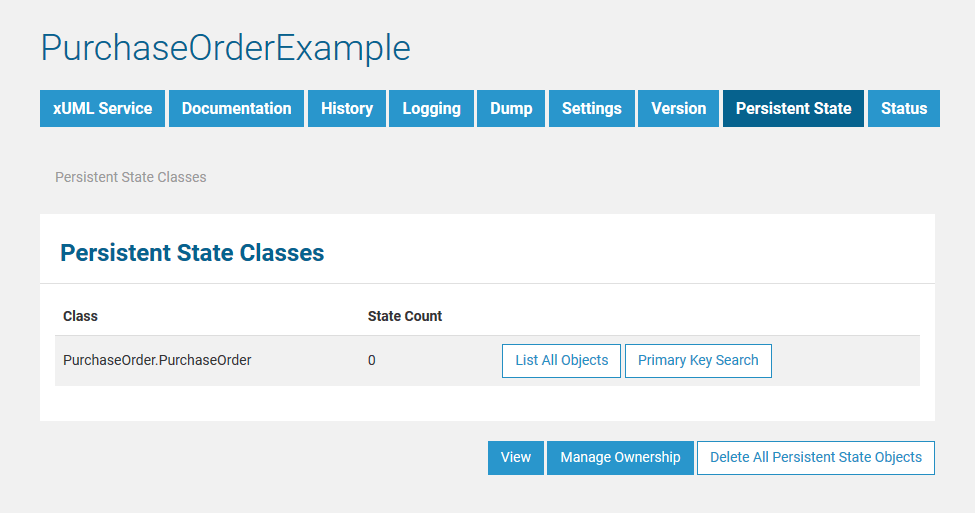
Persistent State Classes
The initial page displays an overview of all persistent state classes and their states, in this example PurchaseOrder. As the xUML service was just started, no states have been created yet and State Count is 0. This is also why no list of all objects can be retrieved and no primary key search can be started. The corresponding buttons are all disabled.
Managing Persistent State Ownership
After creating some Running multiple E2E Bridges, you can setup the system in a way that all Bridges are using the same persistent state database. The persistent state objects (in this database are not only distinguished by their primary persistent state key, but also by a Bridge id reflecting the Bridge that owns these objects.
If a Bridge (Bridge_1) crashes, a redundant service running on another Bridge (Bridge_2) can take over the processing of the persistent state objects. To enable the second Bridge to identify the persistent state objects to process, you have to change the owner of the objects from Bridge_1 to Bridge_2. This can be done by the use of button Manage Ownership.case purchase orders), the new state count is displayed and the two buttons List All Objects and Primary Key Search are activated.
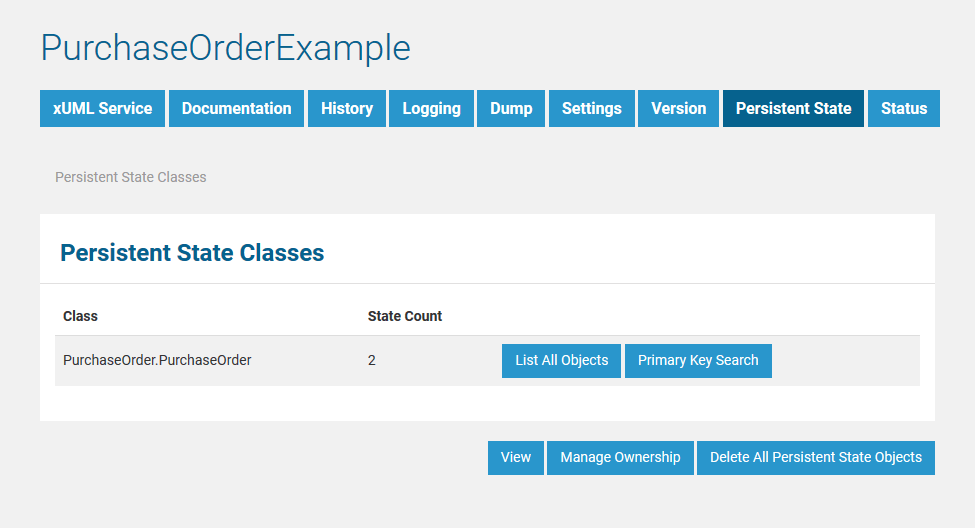
Click List All Objects to view a list of all objects (see section List of All Persistent State Objects). Click Primary Key Search to search for particular persistent state objects by primary key (see section Primary Key Search).
Managing Persistent State Ownership
| Multiexcerpt include | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
For more information on the persistent state ownership concept refer to Persistent State Ownership.
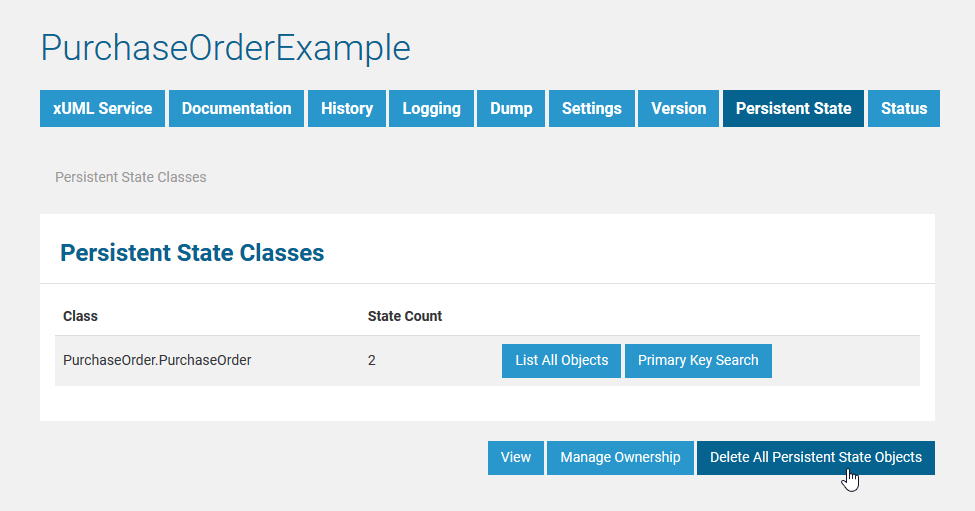
Deleting All Persistent State Objects
Deletion of all persistent state objects is not possible as long as the xUML service is still running. Only users of a group having ADMIN rights may delete all persistent state objects.
| Noteinfo | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
While looking at these screens, the state engine in the background continues to process the objects. Therefore, it can happen that an object or an event does no longer exist when you click on a link. In this case, the Bridge will display an error message. |
| After stopping the xUML service, the button is active. | |
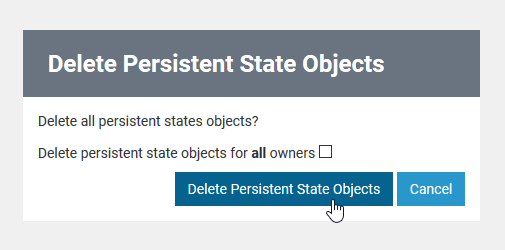
| You need to confirm the removal by clicking Delete Persistent State Objects. You may also Cancel the transaction. |
The checkbox Checkbox Delete persistent state objects for all owners enables you to delete all persistent state objects of the persistent state databasecurrent service - even those that belong to other owners. That includes objects created by other xUML services as the one you just stopped. Only users of a group having ADMIN rights may delete all persistent state objects.
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Handle this option very carefully. The Bridge will not check whether these other xUML services are stopped and just delete all objects. |
After creating some persistent state objects (in this case purchase orders), the new state count is displayed and the two buttons List All Objects and Primary Key Search are activated.
...
all |
...
objects |
...
. |
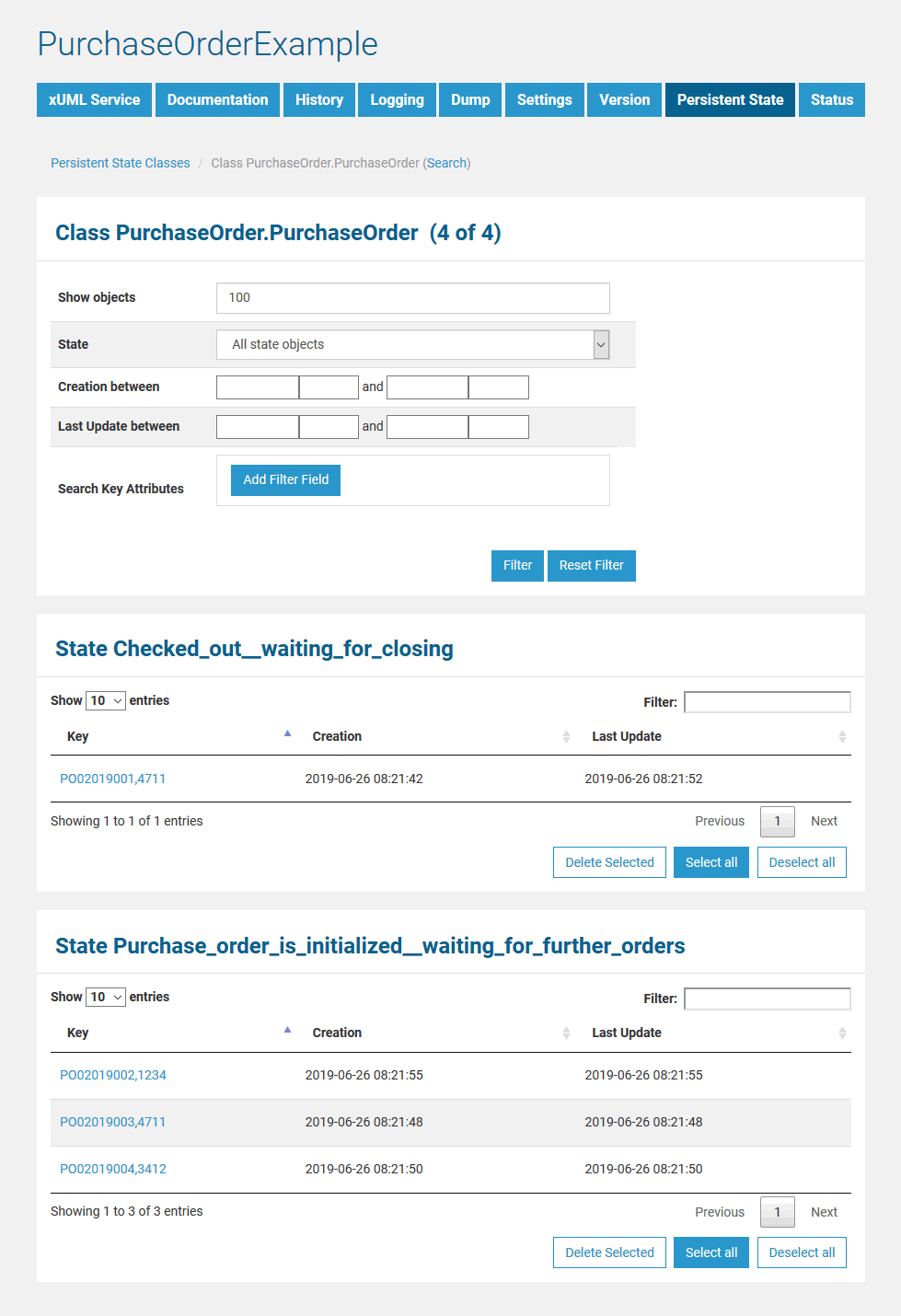
List of All Persistent State Objects
After creating some objects of the persistent state class (e.g. purchase orders), all objects can be listed.
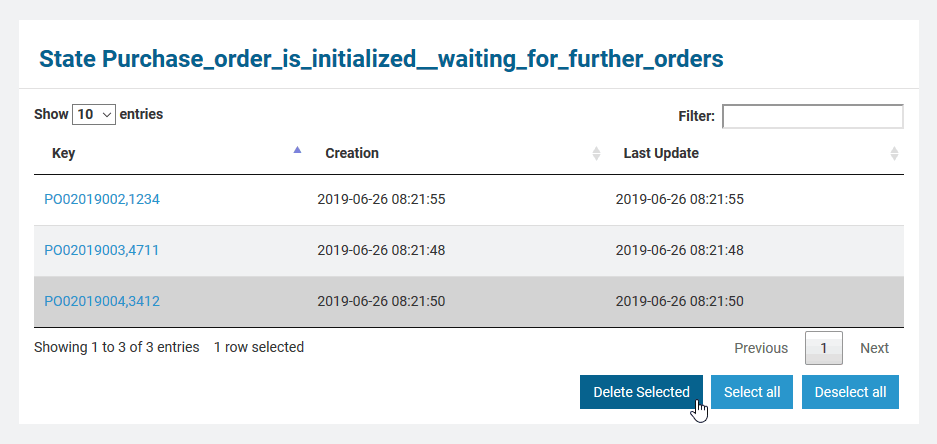
The page is divided into two parts, a filtering part and, below that, a list part. The list part contains separate lists for each state. Click one of the little arrows in the table header of a list to sort the table by the selected column. You can specify the count of rows to be displayed on a page for each table (Show n entries). Click Previous or Next to toggle between pages.
In the persistent state object list, the names of all persistent state elements are displayed in normalized UML. Normalized means, all white spaces are replaced by underscores ('_'). All current persistent state objects of this service are listed, grouped by state and ordered by creation timestamp (latest first). For each persistent state object, you can see primary key, creation date/time and date/time of the last update.
| Noteinfo | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
The name of the final state will never be seen because by entering the final state the object ceases to exist. However, while destroying the object, the state machine is in the state --8<--. Think of --8<-- as an internal state name for the final state. So every object will reach this state before it gets deleted from the database. The state name --8<-- is cryptic by design to prevent a clash with other state names. If the state engine has a low load, you will perhaps never see objects in this state. If the state engine is very busy, you can see a lot of such objects, but this is no problem. |
...
Click Filter to update the screen or Reset Filter to remove all entered data.
| Noteinfo | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
All persistent state information can also be viewed, if the service is stopped. This is helpful in case of debugging a service. But, in this case, browsing the persistent state details may be slower, as for each request the xUML Runtime is started to collect the information and stopped afterwards. The persistent state objects will not be changed in this case! |
...
Make sure to not click the key of the persistent state object. It is a link that will open the object's details.
| Noteinfo | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Only users with ADMIN rights or who are member of the group which owns the xUML service are allowed to delete persistent state objects. |
...
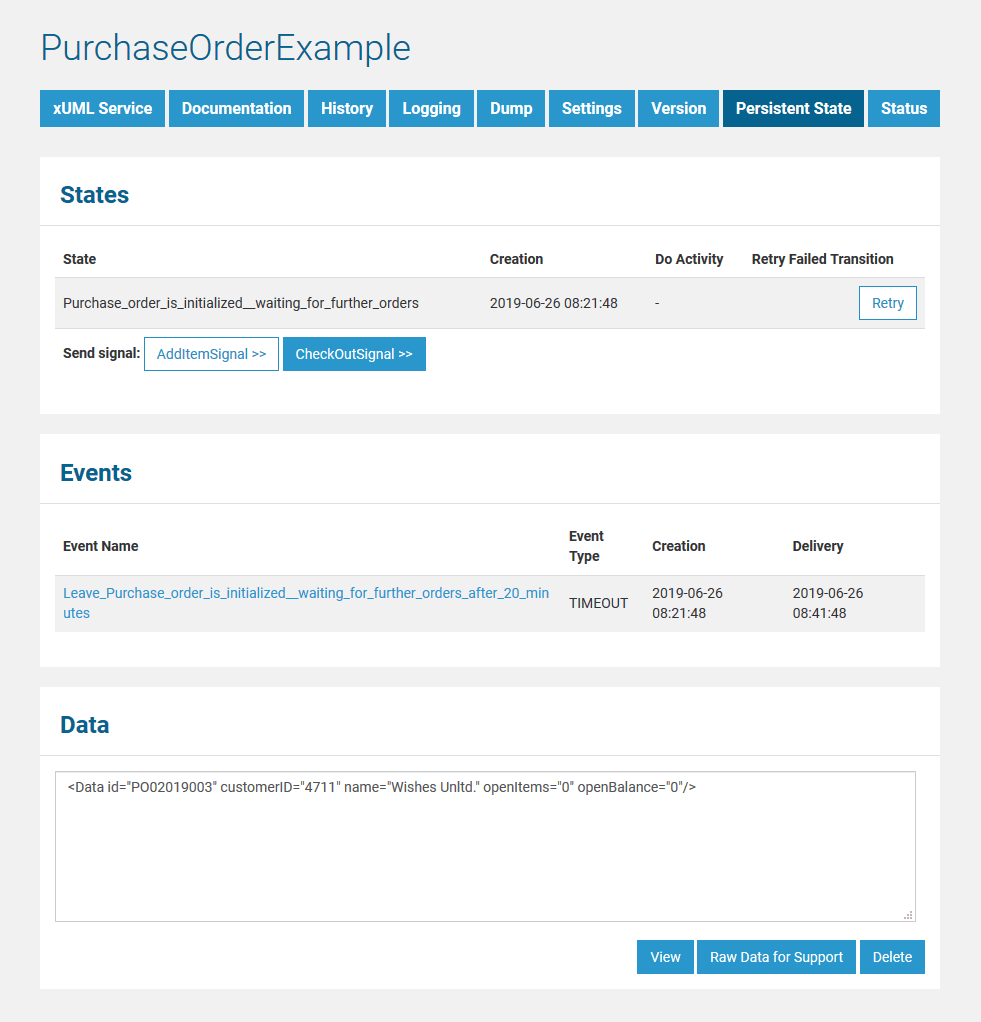
In the persistent state object list, for each persistent state object you can see primary key, creation date/time and date/time of the last update. When clicking on the primary key, more details can be viewed.
The following information is displayed:
| Primary Key | All key fields are displayed, separated by comma. | |||||
| Creation | The timestamp of the creation of the persistent state object. | |||||
| Last Update | The timestamp of the last update of the persistent state object. | |||||
| Owner ID | Owner ID of the service which is owner of the persistent state object. | |||||
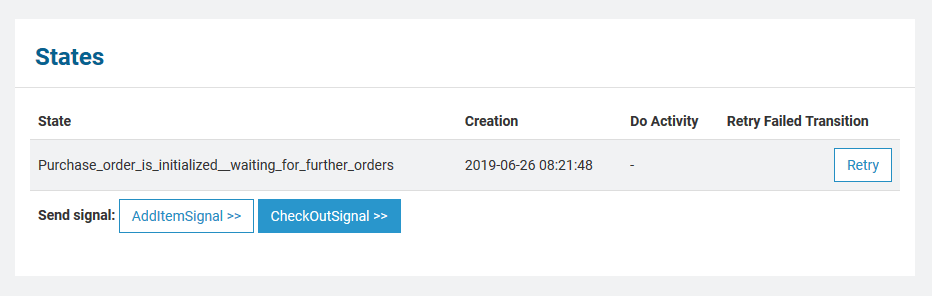
| States | In this group box the state of the persistent state object and all substates are listed with Creation timestamp and the Do Activity the state is performing. The state name is the normalized UML name. Normalized means, all white spaces are replaced by underscores ('_').
| |||||
| Events | A list of all events that occurred on this state object and are not yet finished is displayed. | |||||
| Data | This text box contains the persistent state data, displayed in xml. |
...
- Use Retry to resend the last signal to the persistent state object, if that last transition has failed.
- Click on one of the other buttons to send the indicated signal.
| Noteinfo | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Some signals may be grayed out. This is due to the fact, that at the moment it is only possible to send signals that have no parameters. |
...
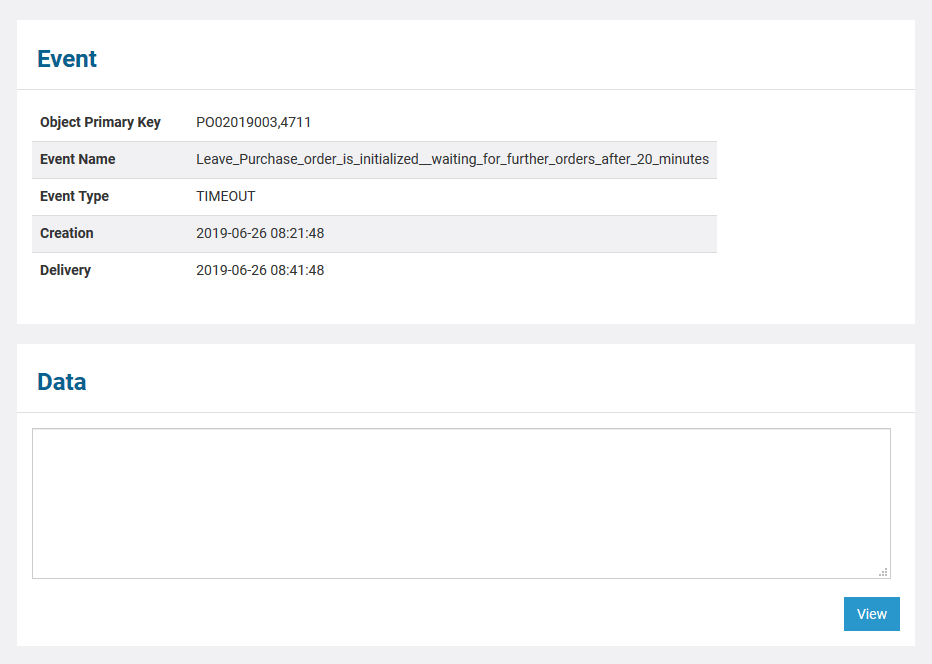
In the persistent state object list, for each persistent state object you can see primary key, creation date/time and date/time of the last update. When clicking on the primary key, more details can be viewed.
The following information is displayed:
| Element | Description | Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Object Primary Key | Key fields of the persistent state object, separated by comma. | ||||
| Event Name | Name of the event. | ||||
| Event Type | Bridge type of the event. | STARTWORK | A do activity is scheduled. | ||
WORKDONE | A do activity has finished and an update to the object is scheduled. | ||||
TIMEOUT | A time triggered transition is scheduled. | ||||
COMPLETION | A regular transition is scheduled. | ||||
JOIN | Parallel persistent states are joined. | ||||
FINALIZE | Object reached final state and is due to be deleted. | ||||
SIGNAL | Processing a signal that has been send to the object. | ||||
| Creation | The timestamp of the creation of the persistent state object. | ||||
| Delivery | The timestamp of when this event has been delivered to the object. | ||||
| Data | This text box contains the persistent state data, displayed in xml. | ||||
Click View to update the screen.